The Flow Resistivity Calculator is a specialized tool used to determine how much resistance a porous material presents to airflow passing through it. This property, known as flow resistivity, is critical in acoustical engineering, insulation design, and material testing. It helps evaluate how well a material can absorb sound or resist air movement, making it essential in applications like soundproofing, HVAC filter design, and automotive acoustics.
By using this calculator, users can quantify the resistance of different materials, allowing engineers and designers to choose the right material for their needs. It also helps in understanding the behavior of fibrous or foam-like substances in airflow conditions. This calculator belongs to the Acoustical and Material Engineering Calculators category.
formula of Flow Resistivity Calculator
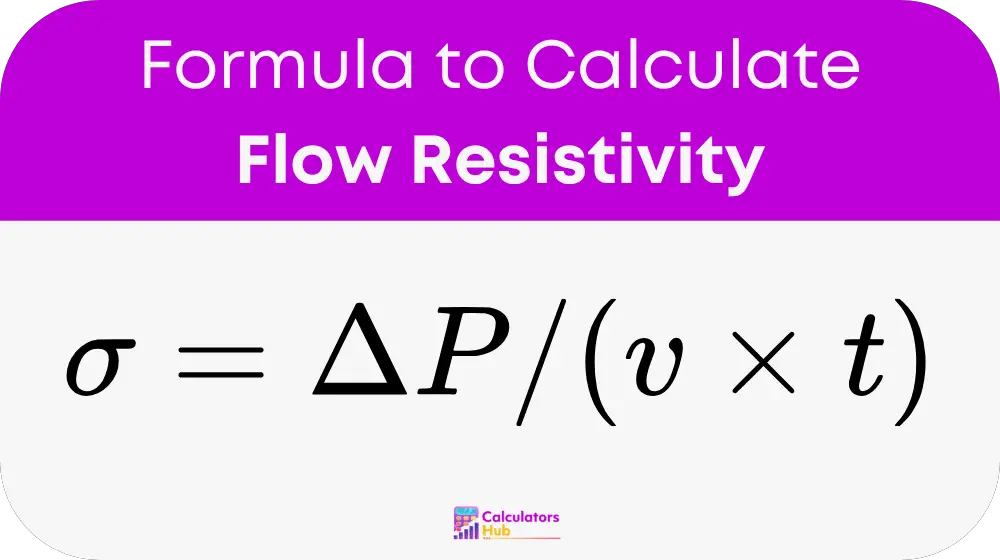
Where:
σ = Flow resistivity (Pa·s/m²)
ΔP = Pressure difference across the material (in Pascals)
v = Particle velocity of air through the material (in m/s)
t = Thickness of the sample (in meters)
Flow resistivity measures the resistance encountered by air as it flows through a unit thickness of porous material. A higher σ value means greater resistance to airflow, which usually corresponds to better sound absorption characteristics in acoustic panels or insulation materials.
Common Flow Resistivity Terms Table
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Flow Resistivity (σ) | Resistance per unit thickness to air flow through a material (Pa·s/m²) |
| Pressure Difference (ΔP) | The pressure applied across the sample material (Pascals) |
| Particle Velocity (v) | Speed of air particles through the material (m/s) |
| Thickness (t) | Thickness of the sample being tested (meters) |
| Sound Absorption | Property influenced by flow resistivity, especially in acoustic materials |
| Porous Material | Material with open spaces that allow air to pass through |
This table helps explain the most important parameters and terms associated with flow resistivity to make calculations easier to understand for beginners and professionals alike.
Example of Flow Resistivity Calculator
Let’s say we are testing a foam panel for use in acoustic insulation. The data collected from the test is as follows:
- Pressure difference across the foam (ΔP) = 200 Pascals
- Air particle velocity through the foam (v) = 0.05 m/s
- Thickness of the foam (t) = 0.02 meters
Using the formula:
σ = ΔP / (v × t)
σ = 200 / (0.05 × 0.02) = 200 / 0.001 = 200000 Pa·s/m²
The flow resistivity of the foam is 200,000 Pa·s/m², which indicates strong resistance to airflow and possibly good acoustic absorption properties. This value can be compare to standards to evaluate its effectiveness in noise control.
Most Common FAQs
Flow resistivity is use to evaluate how a material resists airflow, mainly for purposes like sound absorption, ventilation efficiency, and insulation performance.
Not necessarily. Higher resistivity often improves sound absorption but can reduce airflow in HVAC systems. The ideal value depends on the specific application.
Accurate measurement requires controlled equipment for airflow, pressure, and thickness. However, estimates can be made using typical values for common materials and this calculator.