The Energy to Wavelength Calculator helps users determine the wavelength of a photon or electromagnetic wave based on its energy. This is a critical concept in quantum mechanics, spectroscopy, optics, and photonics. It’s especially useful in physics and chemistry research, solar cell engineering, and the development of LED and laser technologies. This calculator belongs to the Electromagnetic and Quantum Physics Calculator category.
Understanding how energy relates to wavelength allows scientists and engineers to design systems that interact with light and electromagnetic radiation in predictable and precise ways.
Formula of Energy to Wavelength Calculator
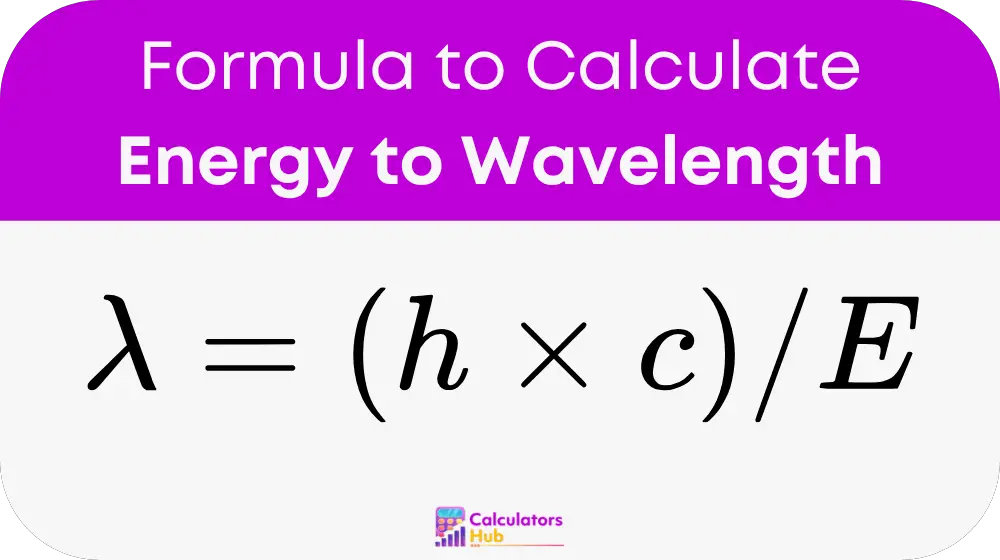
Detailed Breakdown:
- λ = Wavelength, in meters (m)
- h = Planck’s constant = 6.62607015 × 10⁻³⁴ J·s
- c = Speed of light = 2.99792458 × 10⁸ m/s
- E = Energy, in joules (J)
This formula is derived from the relationship between energy and frequency (E = h × f) and the wave equation (c = λ × f). By combining both, we solve for wavelength in terms of energy.
Quick Reference Table
This table provides wavelength values for commonly encountered energy levels in joules. It can help you make quick comparisons without recalculating each time:
| Energy (Joules) | Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|
| 3.2 × 10⁻¹⁹ | 620 |
| 4.14 × 10⁻¹⁹ | 480 |
| 6.63 × 10⁻¹⁹ | 300 |
| 1.99 × 10⁻¹⁸ | 100 |
| 1.99 × 10⁻¹⁶ | 1 |
Note: To convert meters to nanometers (nm), multiply the result by 1 × 10⁹.
Example of Energy to Wavelength Calculator
Let’s calculate the wavelength of a photon with an energy of 4 × 10⁻¹⁹ joules.
Step 1:
Use the formula:
λ = (6.62607015 × 10⁻³⁴ × 2.99792458 × 10⁸) / 4 × 10⁻¹⁹
Step 2:
Numerator: h × c = 1.98644586 × 10⁻²۵ J·m
Denominator: 4 × 10⁻¹⁹ J
λ = 1.98644586 × 10⁻²۵ / 4 × 10⁻¹⁹ = 4.97 × 10⁻⁷ m = 497 nm
So, the wavelength is approximately 497 nanometers, which falls within the green portion of the visible spectrum.
Most Common FAQs
It helps convert photon energy to wavelength, which is essential in laser design, spectroscopy, and analyzing light interactions with matter.
Always input energy in joules for accurate results. If you have energy in electronvolts (eV), convert it using:
1 eV = 1.602 × 10⁻¹⁹ J
Yes. This calculator works across all ranges of electromagnetic radiation—from radio waves to gamma rays—if energy values are correctly entered in joules.