The Energy to Vaporize Calculator is designed to calculate the amount of thermal energy needed to convert a given mass of a substance from a liquid to a gaseous state at its boiling point. This calculation is essential in thermal engineering, chemical processing, HVAC design, and environmental science. The tool is based on the latent heat of vaporization, a physical constant specific to each substance. This calculator belongs to the Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer Calculator category.
By knowing the exact energy needed for vaporization, engineers and researchers can better design heating systems, analyze phase transitions, and control energy consumption during boiling or distillation processes.
Formula of Energy To Vaporize Calculator
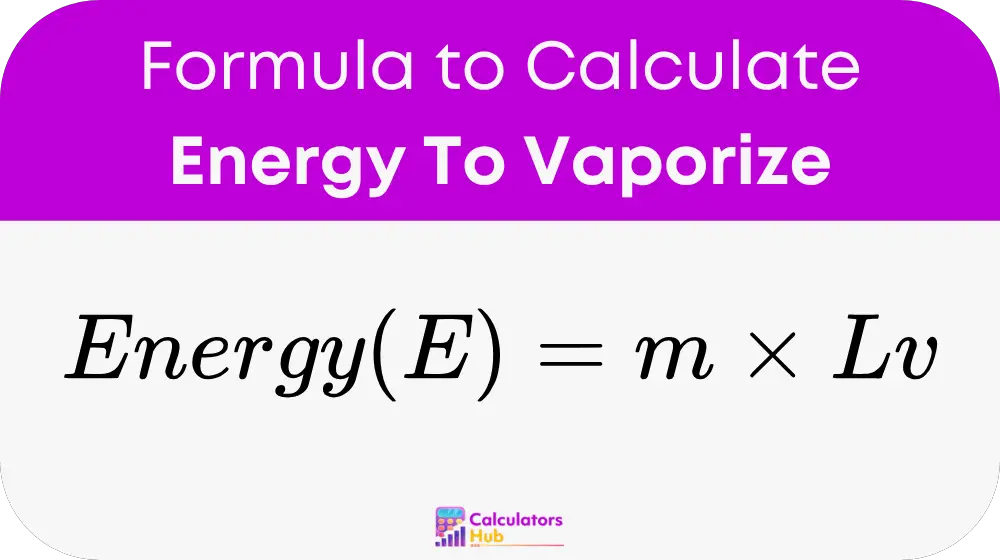
Detailed Breakdown:
- E = Energy required to vaporize the substance (in joules, J)
- m = Mass of the substance (in kilograms, kg)
- Lv = Latent heat of vaporization (in joules per kilogram, J/kg)
Latent heat of vaporization represents the amount of energy needed to turn 1 kilogram of a substance from liquid to gas without a temperature change. This value varies depending on the material being vaporized.
Quick Reference Table
Here is a table listing common substances with their latent heat of vaporization to help users quickly estimate energy requirements without needing to look up constants every time:
| Substance | Latent Heat of Vaporization (J/kg) | Energy for 1 kg (J) |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 2,260,000 | 2,260,000 |
| Ethanol | 841,000 | 841,000 |
| Ammonia | 1,370,000 | 1,370,000 |
| Benzene | 393,000 | 393,000 |
| Acetone | 518,000 | 518,000 |
This data can be used directly with the formula by multiplying the specific Lv by the mass in kilograms.
Example of Energy To Vaporize Calculator
Suppose you want to calculate the energy required to vaporize 2.5 kilograms of water.
Step 1:
Use the latent heat of vaporization for water: Lv = 2,260,000 J/kg
Step 2:
Use the formula:
E = m × Lv = 2.5 × 2,260,000 = 5,650,000 J
So, the energy required to vaporize 2.5 kg of water is 5,650,000 joules.
Most Common FAQs
Yes, as long as you know the correct latent heat of vaporization for the specific substance. Always ensure values are in consistent units (J/kg for Lv and kg for mass).
No. This calculator only computes the energy needed to vaporize the liquid once it is already at its boiling temperature. Additional energy would be required to heat the liquid to that point.
Water has a high latent heat due to strong hydrogen bonding between molecules. This makes it efficient for heat transfer but also energy-intensive to boil.