The Electrostatic Interaction Energy Calculator is a scientific tool used to determine the potential energy between two charged particles based on their charges and the distance between them. This type of energy is a result of electrostatic forces, which are described by Coulomb’s Law. The calculator simplifies the process of evaluating the attraction or repulsion between charges in electric fields.
This tool is particularly useful in fields like physics, chemistry, materials science, and electrical engineering. It helps students, researchers, and professionals model interactions at the atomic and molecular level, analyze energy within capacitors, or understand bonding forces between ions.
Formula of Electrostatic Interaction Energy Calculator
To calculate electrostatic interaction energy, use Coulomb’s Law:
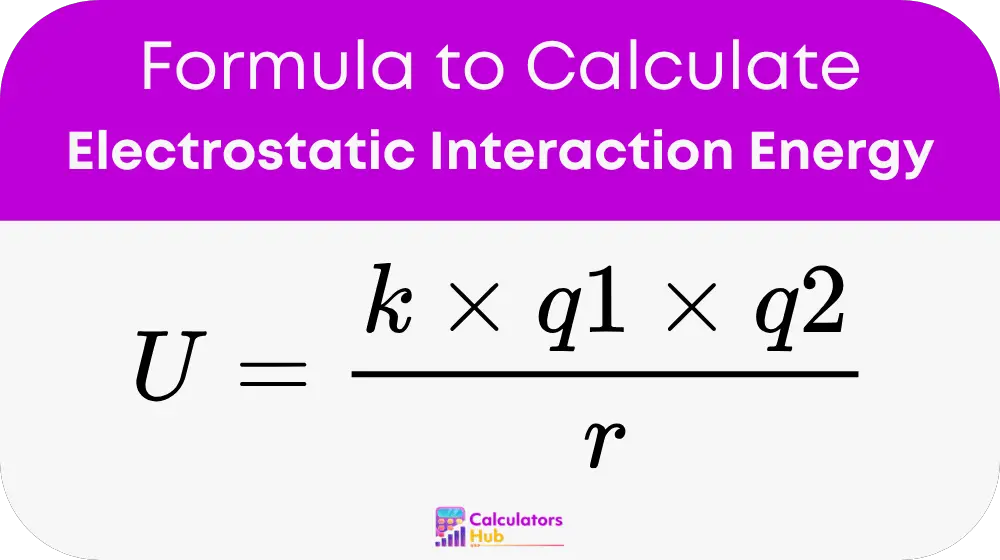
Where:
- U is the electrostatic interaction energy (in joules)
- k is Coulomb’s constant = 8.988 × 10⁹ N·m²/C²
- q1 is the charge of the first particle (in coulombs)
- q2 is the charge of the second particle (in coulombs)
- r is the distance between the particles (in meters)
The resulting value can be positive or negative. A positive value indicates repulsion (like charges), while a negative value indicates attraction (opposite charges).
General Terms Related to Electrostatic Energy
Below is a table with commonly used terms and their meanings, helpful for users exploring or using this calculator.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Electrostatic Energy (U) | The potential energy stored due to interaction between two static charges |
| Coulomb’s Constant (k) | A proportionality constant in electrostatics (8.988 × 10⁹ N·m²/C²) |
| Charge (q) | The quantity of electric charge measured in coulombs (C) |
| Distance (r) | The straight-line distance between the two charges (in meters) |
| Coulomb’s Law | A fundamental law describing electrostatic force and energy |
| Potential Energy | The stored energy based on position in an electric field |
| Like Charges | Charges with the same sign that repel each other |
| Opposite Charges | Charges with opposite signs that attract each other |
These definitions help in understanding how the values and constants affect the result of the electrostatic interaction.
Example of Electrostatic Interaction Energy Calculator
Let’s calculate the electrostatic interaction energy between two particles.
Given:
- q1 = 2 × 10⁻⁶ C
- q2 = -3 × 10⁻⁶ C
- r = 0.05 meters
Step 1: Apply the formula
U = (k × q1 × q2) / r
Substitute the values:
U = (8.988 × 10⁹) × (2 × 10⁻⁶) × (-3 × 10⁻⁶) / 0.05
U = (8.988 × 10⁹) × (-6 × 10⁻¹²) / 0.05 ≈ -1.0786 joules
The negative sign indicates that the interaction is attractive since the charges are opposite.
This example demonstrates how the sign and magnitude of the energy reveal the nature and strength of the electrostatic interaction.
Most Common FAQs
A negative value indicates that the two charges attract each other. This happens when one is positive and the other is negative, leading to a stable interaction that releases energy.
It helps in predicting the energy involved in molecular interactions, the behavior of charged particles in electric fields, and energy storage in electrical systems like capacitors or sensors.
Yes, when both charges are the same sign (either positive or negative), the electrostatic energy is positive, indicating a repulsive force between them.