The Destructive Frequency Calculator helps engineers, physicists, and designers determine the frequency at which an object or structure experiences destructive resonance. Resonance occurs when an external force matches the natural frequency of an object, leading to excessive vibrations that can result in structural failure. By using this calculator, users can analyze potential risks and take preventive measures in mechanical systems, buildings, and other structures.
Formula
The destructive frequency is calculated using the following formula:
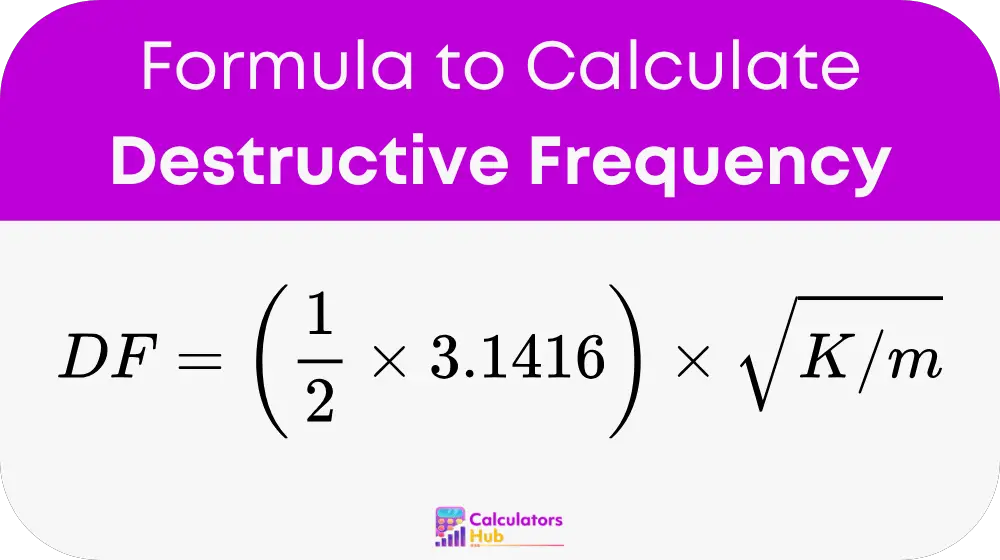
where:
- K (Stiffness) is the structural stiffness, typically measured in Newtons per meter (N/m).
- m (Mass) is the mass of the vibrating object, typically in kilograms (kg).
- π (Pi) is approximately 3.1416.
This formula helps engineers assess vibration risks and design structures to withstand destructive frequencies.
Destructive Frequency Reference Table
This table provides estimated destructive frequencies for different stiffness and mass values.
| Stiffness (N/m) | Mass (kg) | Destructive Frequency (Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 5 | 7.12 |
| 5000 | 10 | 11.25 |
| 10000 | 20 | 11.25 |
| 20000 | 25 | 14.14 |
| 50000 | 50 | 15.92 |
These values serve as a reference for determining potential vibration risks in various structures and mechanical systems.
Example of Destructive Frequency Calculator
An engineer is analyzing a system where the structural stiffness is 10,000 N/m, and the mass of the vibrating object is 20 kg. Using the formula:
Destructive Frequency = (1 / 2 × 3.1416) × √(10,000 / 20)
= (1 / 6.2832) × √(500)
≈ 0.159 × 22.36 ≈ 3.56 Hz
This means that the system could experience destructive resonance at approximately 3.56 Hz, requiring adjustments to avoid potential failure.
Most Common FAQs
Destructive frequency analysis helps engineers design structures and machinery that avoid excessive vibrations, preventing mechanical failure and structural collapse.
An increase in mass lowers the destructive frequency, while a decrease in mass raises it. Adjusting mass is one way to control resonance effects in mechanical systems.
Yes, destructive frequency calculations are essential in civil engineering to ensure that buildings, bridges, and other structures can withstand external forces such as wind, earthquakes, and machinery vibrations.