–
A CTE (Coefficient of Thermal Expansion) Calculator helps engineers, material scientists, and researchers determine how much a material expands or contracts when exposed to temperature changes. The coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is a crucial property of materials used in construction, manufacturing, aerospace, and automotive industries.
Understanding the CTE of a material is essential for preventing structural failures, designing thermal-resistant components, and ensuring compatibility between materials that undergo temperature variations.
This calculator simplifies the process of determining how much a material will change in size based on its CTE value, initial length, and temperature variation.
Formula
The coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is calculated using the following formula:
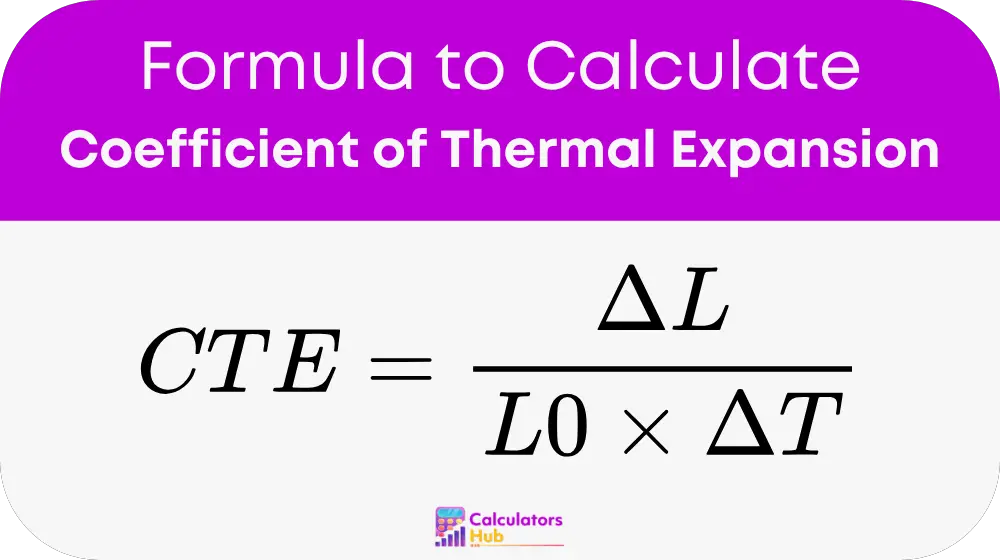
Where:
- CTE is the coefficient of thermal expansion (expressed in per degree Celsius or per degree Kelvin, typically denoted as 1/°C or 1/K).
- ΔL is the change in length (final length - initial length, measured in meters or other units of length).
- L0 is the original length of the material (in meters or other units of length).
- ΔT is the change in temperature (final temperature - initial temperature, measured in degrees Celsius or Kelvin).
This formula allows users to determine the material’s expansion or contraction behavior under different thermal conditions.
Pre-Calculated CTE Values for Common Materials
To help users quickly reference CTE values for various materials, here is a table of typical coefficients of thermal expansion:
| Material | CTE (1/°C) × 10⁶ | CTE (1/K) × 10⁶ |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 23.1 | 23.1 |
| Copper | 16.5 | 16.5 |
| Steel (carbon) | 11.7 | 11.7 |
| Stainless Steel | 16.0 | 16.0 |
| Concrete | 10.0 | 10.0 |
| Glass | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| Silicon | 2.6 | 2.6 |
This table provides a quick reference for engineers and designers who need to account for thermal expansion in their projects.
Example
Let’s calculate the expansion of an aluminum rod that is initially 1.5 meters long when the temperature increases from 25°C to 75°C.
Given:
- L0 = 1.5 meters
- ΔT = 75 - 25 = 50°C
- CTE for aluminum = 23.1 × 10⁻⁶ 1/°C
Applying the formula:
ΔL = CTE × L0 × ΔT
ΔL = (23.1 × 10⁻⁶) × (1.5) × (50) = 0.00173 meters (or 1.73 mm)
So, the aluminum rod expands by 1.73 mm when exposed to a 50°C temperature increase.
Most Common FAQs
CTE helps engineers predict how materials will expand or contract due to temperature changes. This is critical for structural integrity, component fit, and thermal stress management in engineering applications.
Yes, the CTE of a material can change based on temperature range, manufacturing process, and material purity. Some materials exhibit nonlinear expansion at extreme temperatures.