The Critical Curve Speed Calculator is a tool designed to calculate the maximum safe speed at which a vehicle can navigate a curve without losing traction or skidding. It considers factors such as the radius of the curve, the friction between the tires and the road, and the force of gravity. This tool is essential for road safety analysis, vehicle dynamics research, and engineering applications, ensuring that roads and vehicles are designed for optimal performance and safety.
Formula of Critical Curve Speed Calculator
The formula for calculating critical curve speed is:
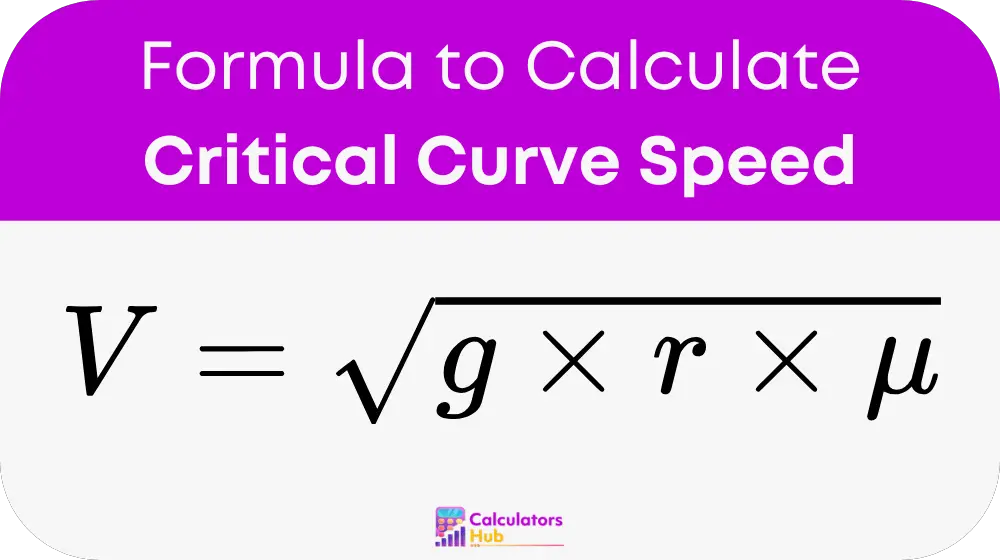
Where:
- V is the critical curve speed (in meters per second or m/s).
- g is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.81 m/s²).
- r is the radius of the curve (in meters).
- μ is the coefficient of friction between the tires and the road surface (a unitless number, typically between 0.5 and 1.0 for normal road conditions).
This formula helps determine the speed at which a vehicle can safely travel around a curve, given specific conditions.
General Terms Table
Below is a table summarizing typical values and terms used in critical curve speed calculations:
| Term | Typical Values | Description |
|---|---|---|
| g (Gravity) | 9.81 m/s² | Acceleration due to gravity |
| r (Curve Radius) | 50-500 meters (depending on the road) | The radius of the curve |
| μ (Friction Coefficient) | 0.5-1.0 (dry roads) or 0.1-0.3 (wet roads) | Friction between tires and the road surface |
| V (Critical Speed) | Varies (calculated value) | Maximum safe speed around the curve |
This table provides context for the variables involved and helps users understand the inputs required for accurate calculations.
Example of Critical Curve Speed Calculator
Let’s calculate the critical curve speed for a vehicle navigating a curve with the following parameters:
- Curve Radius (r): 100 meters
- Coefficient of Friction (μ): 0.8 (dry road)
- Gravity (g): 9.81 m/s²
Step 1: Apply the Formula
V = √(9.81 × 100 × 0.8)
V ≈ 28 m/s
Step 2: Convert to km/h
To convert meters per second to kilometers per hour, multiply by 3.6:
28 m/s × 3.6 = 100.8 km/h
The critical curve speed for this scenario is approximately 100.8 km/h.
Most Common FAQs
The critical curve speed depends on the radius of the curve, the coefficient of friction, and the gravitational constant. Road conditions, such as wet or icy surfaces, can significantly lower the coefficient of friction, reducing the critical speed.
The coefficient of friction is determined by the type of road surface and tire material. Typical values range from 0.5-1.0 for dry surfaces and 0.1-0.3 for wet or icy conditions.
Understanding critical curve speed helps engineers design safe roads by determining appropriate speed limits and curve banking angles, minimizing the risk of accidents.