The Compressive Strength Calculator is a tool that determines the compressive strength of a material, which is the capacity of the material to withstand compressive forces without failing. It is a vital calculation in engineering, construction, and material science, used to evaluate materials like concrete, steel, and ceramics. The tool provides accurate insights into how much pressure a material can bear, ensuring its suitability for structural applications.
Why Is It Important?
Compressive strength is a critical parameter for materials subjected to loads or forces that push them together. It helps engineers and designers assess the structural integrity and durability of materials under real-world conditions. Accurate compressive strength measurements prevent structural failures and ensure safety.
Formula of Compressive Strength Calculator
The Compressive Strength Calculator uses the following formula:
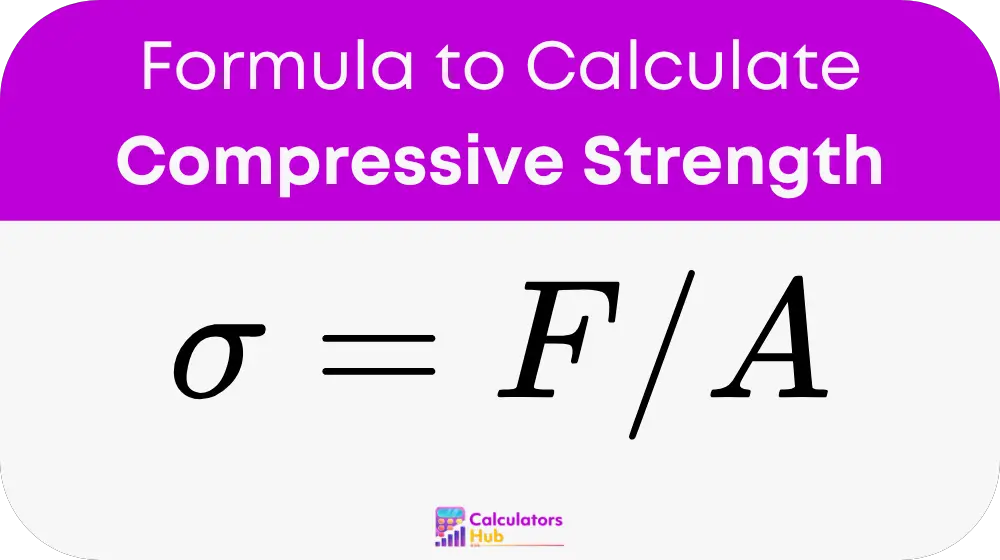
Variables
- σ: Compressive strength (Pascals, psi, or other units of pressure).
- F: Applied force (Newtons or pounds-force).
- A: Cross-sectional area (square meters or square inches).
Steps to Calculate
- Measure or Determine the Applied Force (F):
The force applied during testing, typically measured in Newtons (N) or pounds-force (lbf). - Measure the Cross-Sectional Area (A):
- For circular cross-sections:
A = π × r², where r is the radius of the cross-section. - For rectangular cross-sections:
A = width × height.
- For circular cross-sections:
- Substitute Into the Formula:
Divide the applied force (F) by the cross-sectional area (A) to calculate compressive strength.
Pre-calculated Table for Common Materials
Below is a table showing compressive strength values for common materials:
| Material | Typical Compressive Strength (MPa) | Typical Compressive Strength (psi) |
|---|---|---|
| Concrete | 20–40 | 2,900–5,800 |
| Steel | 250–400 | 36,000–58,000 |
| Aluminum | 70–80 | 10,000–11,600 |
| Brick | 10–50 | 1,450–7,250 |
This table provides quick reference values for engineers and architects.
Example of Compressive Strength Calculator
Scenario
A concrete cylinder with a radius of 0.1 meters is tested under a compressive load of 5,000 Newtons. Calculate the compressive strength.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Determine the Applied Force (F):
F = 5,000 N. - Measure the Cross-Sectional Area (A):
For a circular cross-section:
A = π × r²
A = 3.1416 × (0.1)²
A ≈ 0.0314 m². - Apply the Formula:
σ = F / A
σ = 5,000 / 0.0314
σ ≈ 159,155.03 Pascals (or 159.16 kPa).
Thus, the compressive strength of the concrete cylinder is approximately 159.16 kPa.
Most Common FAQs
This calculator helps determine the maximum pressure a material can withstand under compressive forces, ensuring its suitability for structural applications.
Yes, but you must calculate the cross-sectional area (A) for the specific shape before applying the formula.
Compressive strength ensures that materials like concrete and steel can support loads without collapsing, ensuring safety and structural integrity.