The Compressed Air Velocity Calculator is a tool used to determine the velocity of air flowing through a pipe or duct based on pressure differences and air density. It is essential for optimizing the design and operation of pneumatic systems, ensuring safety, and improving efficiency. This calculator simplifies the complex calculations required for determining air velocity in real-world applications.
Why Is It Important?
Understanding compressed air velocity is crucial for system performance and safety. High velocities can cause turbulence, pressure drops, and wear in pipelines, while low velocities may lead to inefficiencies. This calculator ensures accurate velocity measurements, helping engineers design effective systems and troubleshoot problems.
Formula of Compressed Air Velocity Calculator
The Compressed Air Velocity Calculator uses the following formula:
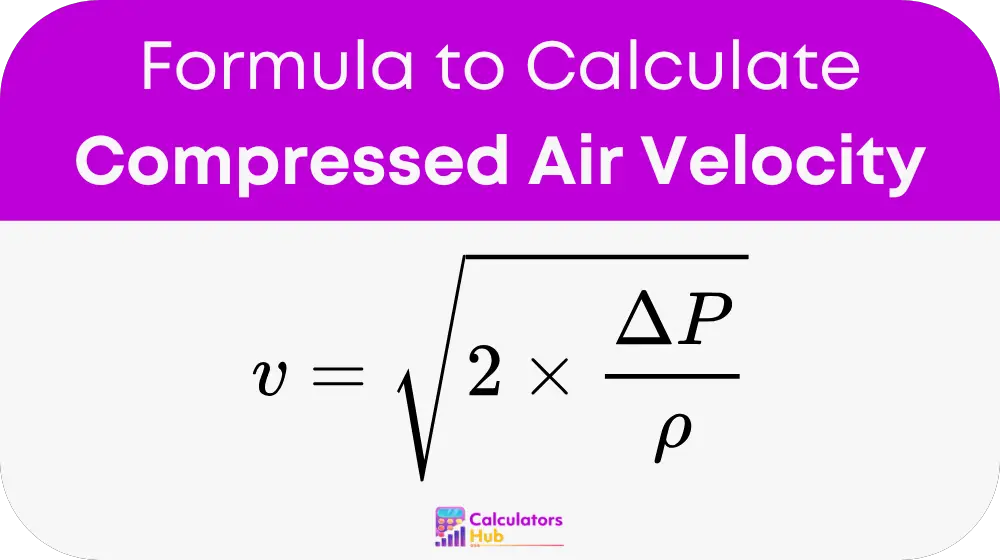
Variables
- v: Velocity of the compressed air (meters per second).
- ΔP: Pressure difference driving the flow (P₁ - P₂), in Pascals.
- ρ: Density of the air (kilograms per cubic meter, kg/m³).
Steps to Calculate
- Calculate the Pressure Difference (ΔP):
ΔP = P₁ - P₂- P₁ = upstream absolute pressure (Pascals).
- P₂ = downstream absolute pressure (Pascals).
- Determine the Density of Compressed Air (ρ):
Use the ideal gas law to calculate air density:
ρ = P / (R × T)- P = absolute pressure of the air (Pascals).
- R = specific gas constant for air (287 J/kg·K).
- T = absolute temperature of the air (Kelvin).
- Substitute into the Velocity Formula:
Use the calculated values of ΔP and ρ in the formula v = √(2 × ΔP / ρ).
Pre-calculated Table for Common Scenarios
Below is a table providing pre-calculated air velocities for typical scenarios in pneumatic systems:
| Pressure Difference (ΔP, Pascals) | Air Temperature (°C) | Air Density (kg/m³) | Velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | 25 | 1.17 | 29.2 |
| 1000 | 25 | 1.17 | 41.3 |
| 2000 | 30 | 1.15 | 57.9 |
| 5000 | 40 | 1.10 | 95.5 |
This table provides a quick reference for engineers and technicians, saving time on manual calculations.
Example of Compressed Air Velocity Calculator
Scenario
Calculate the velocity of compressed air flowing through a pipe with a pressure difference of 2000 Pascals. The air temperature is 30°C, and the upstream absolute pressure is 1.5 bar.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Convert Temperature to Kelvin:
T = 30 + 273.15 = 303.15 K - Calculate Air Density (ρ):
P = 1.5 bar = 1.5 × 10⁵ Pascals
R = 287 J/kg·K
ρ = P / (R × T) = (1.5 × 10⁵) / (287 × 303.15) ≈ 1.71 kg/m³ - Determine the Pressure Difference (ΔP):
ΔP = 2000 Pascals - Apply the Velocity Formula:
v = √(2 × ΔP / ρ)
v = √(2 × 2000 / 1.71)
v ≈ √(2339.18) ≈ 48.37 m/s
Thus, the velocity of the compressed air is approximately 48.37 m/s.
Most Common FAQs
This calculator helps determine the speed of air flow in pneumatic systems, ensuring optimal performance and safety in industrial applications.
The calculator is highly accurate as long as the input values (pressure, temperature, and air properties) are correct and measured precisely.
Yes, but you must use the appropriate specific gas constant (R) for the gas being analyzed.