The Coefficient of Velocity (Cv) Calculator measures the efficiency of a fluid passing through an orifice. It determines how closely the actual velocity of the fluid matches its theoretical velocity, which is calculated using Bernoulli’s equation. This tool is essential in fluid mechanics, helping engineers assess flow efficiency and identify losses due to factors like friction or turbulence.
By quantifying the ratio of actual to theoretical velocity, this calculator simplifies performance analysis of nozzles, orifices, and other fluid control devices.
Formula of Coefficient of Velocity Calculator
The formula for calculating the coefficient of velocity (Cv) is:
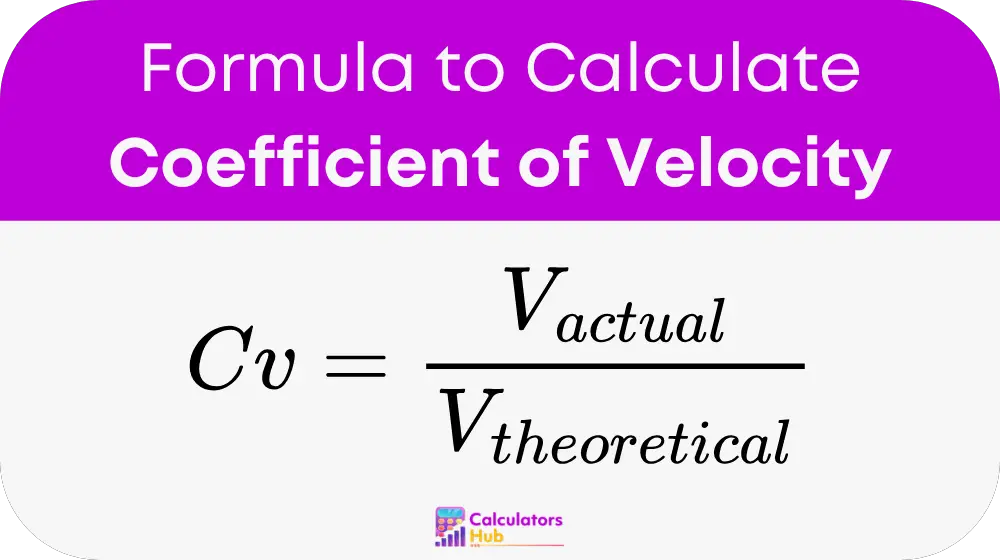
Where:
- Cv = Coefficient of velocity
- V_actual = Actual velocity of the fluid passing through the orifice
- V_theoretical = Theoretical velocity of the fluid, derived using Bernoulli's equation
Detailed Formulas for Variables:
1. Theoretical Velocity (V_theoretical):
V_theoretical = √(2 × g × h)
Where:
- g = Acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s²)
- h = Head or height of the fluid column above the orifice (in meters)
2. Actual Velocity (V_actual):
V_actual = Q / A
Where:
- Q = Actual volumetric flow rate (in cubic meters per second)
- A = Cross-sectional area of the orifice (in square meters), calculated as:
A = π × (d / 2)²- d = Diameter of the orifice (in meters)
Substitute the calculated values for theoretical and actual velocities into the Cv formula to determine the coefficient of velocity.
Table for Common Scenarios
This table provides pre-calculated values for typical fluid flow scenarios.
| Orifice Diameter (m) | Fluid Head (m) | Volumetric Flow Rate (Q, m³/s) | Theoretical Velocity (m/s) | Actual Velocity (m/s) | Coefficient of Velocity (Cv) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 2 | 0.002 | 6.26 | 5.95 | 0.95 |
| 0.1 | 1.5 | 0.005 | 5.42 | 5.15 | 0.95 |
| 0.08 | 3 | 0.004 | 7.67 | 7.3 | 0.95 |
| 0.06 | 2.5 | 0.003 | 7.00 | 6.65 | 0.95 |
This reference helps users estimate Cv values without performing calculations for commonly encountered conditions.
Example of Coefficient of Velocity Calculator
Let’s calculate the coefficient of velocity for a fluid flow scenario:
- Orifice diameter (d) = 0.05 m
- Head of fluid (h) = 2 m
- Volumetric flow rate (Q) = 0.002 m³/s
Step 1: Calculate the Cross-Sectional Area (A)
A = 3.1416 × (0.05 / 2)²
A = 3.1416 × 0.000625 = 0.00196 m²
Step 2: Calculate the Theoretical Velocity (V_theoretical)
V_theoretical = √(2 × 9.81 × 2)
V_theoretical = √39.24 = 6.26 m/s
Step 3: Calculate the Actual Velocity (V_actual)
V_actual = 0.002 / 0.00196
V_actual = 5.95 m/s
Step 4: Calculate the Coefficient of Velocity (Cv)
Cv = 5.95 / 6.26
Cv = 0.95
The coefficient of velocity is 0.95, indicating that the actual velocity is 95% of the theoretical velocity.
Most Common FAQs
The coefficient of velocity quantifies the efficiency of fluid flow through an orifice, helping identify losses due to factors like friction or turbulence. It is crucial for optimizing the design of fluid systems.
A Cv value close to 1 indicates high efficiency, meaning the actual velocity closely matches the theoretical velocity with minimal losses.
Yes, the calculator can be applied to gases, provided the appropriate parameters like density and flow rate are adjusted for gas properties.