The Audio Frequency Speed Calculator is an essential tool for audio engineers, acoustics researchers, and physics educators. It calculates the speed of sound in a medium by utilizing the frequency and wavelength of an audio wave. This calculator is crucial for designing sound systems, optimizing acoustics in buildings, and educational purposes to demonstrate how sound travels through various environments.
Formula of Audio Frequency Speed Calculator
The formula to calculate the speed of sound based on its frequency and wavelength is:
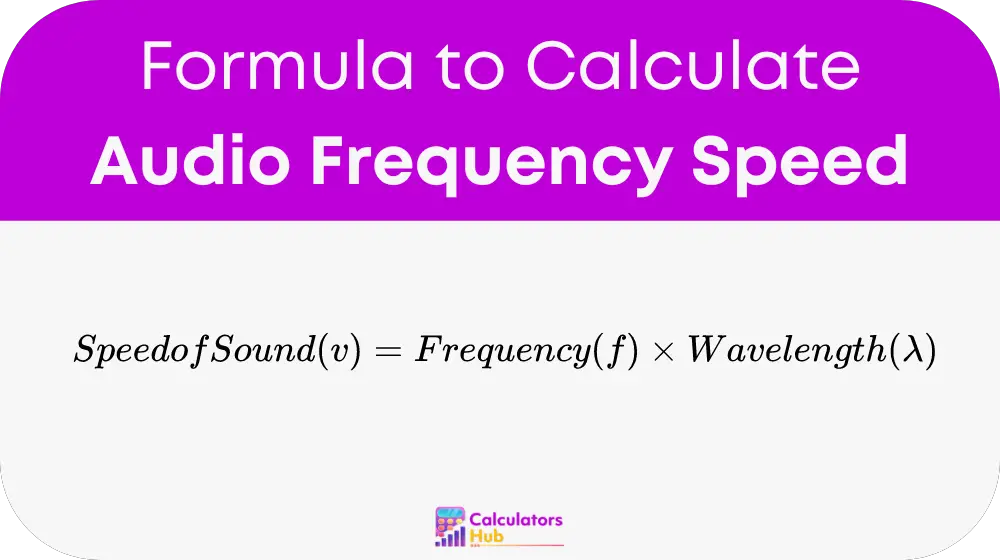
Where:
- Frequency (f): The number of oscillations or cycles per second, measured in Hertz (Hz).
- Wavelength (λ): The distance between successive crests of a wave, typically measured in meters (m).
This formula helps determine how fast sound waves travel through different mediums, which is vital for various applications in both audio production and scientific research.
Table of General Terms
Here’s a table of key terms associated with the Audio Frequency Speed Calculator to enhance understanding:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Speed of Sound | The rate at which sound waves pass through a medium, measured in meters per second (m/s). |
| Frequency | The number of complete oscillations or cycles of a wave per second, measured in Hertz (Hz). |
| Wavelength | The distance between consecutive crests or troughs in a wave, measured in meters (m). |
Example of Audio Frequency Speed Calculator
To illustrate, consider a scenario where you need to calculate the speed of sound in air at a frequency of 1 kHz (1,000 Hz) and a wavelength of 0.34 meters:
Speed of Sound (v) = 1,000 Hz * 0.34 m = 340 m/s
This example shows that sound travels at 340 meters per second under these conditions, which is roughly the speed of sound in air at room temperature.
Most Common FAQs
It is a tool used to calculate the speed at which sound travels through a medium based on the frequency and wavelength of the sound.
Knowing the speed of sound is crucial for applications such as room acoustics, speaker placement, and audio system design, ensuring optimal sound quality and performance.
The medium through which sound travels—air, water. solids—affects its speed due to variations in density and elastic properties. Sound travels faster in solids and slowest in gases.