The Angle Drop Calculator is an essential tool used in various fields such as engineering, construction, and physics to calculate the vertical drop of an object when the horizontal distance and angle of declination are known. This tool is particularly useful for professionals who need to plan or analyze projects that involve slopes, such as road construction, pipeline installation, and architectural design.
Formula of Angle Drop Calculator
The calculation of vertical drop (D) is based on trigonometric principles:
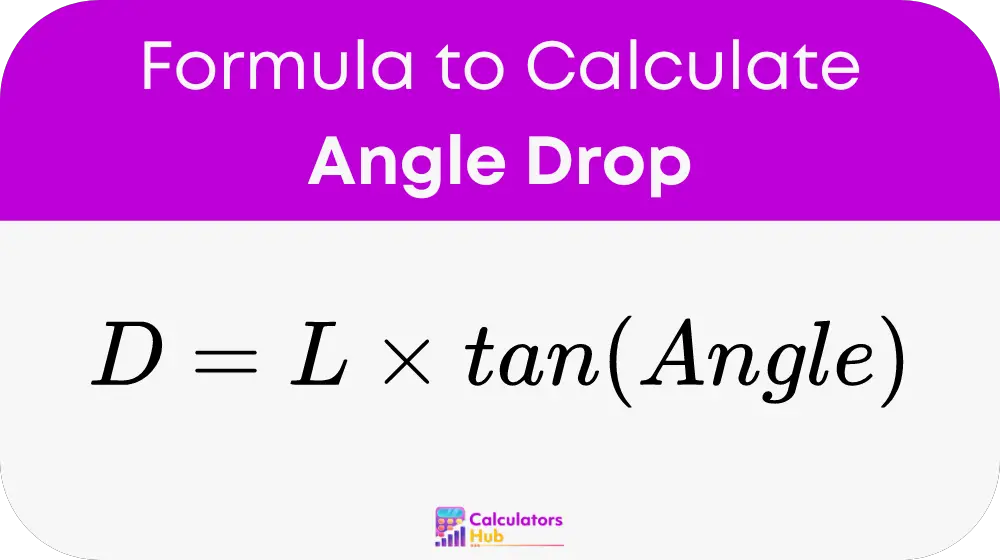
Where:
- D is the vertical drop.
- L is the horizontal distance.
- Angle is the angle of inclination or declination.
Steps for Calculation:
- Convert the Angle from Degrees to Radians if Necessary:
- Angle in Radians = Angle in Degrees * (π / 180)
- Calculate the Tangent of the Angle:
- tan(Angle) = opposite / adjacent
- Multiply the Horizontal Distance (L) by the Tangent of the Angle to Get the Vertical Drop (D):
- D = L * tan(Angle)
Detailed Process:
- Convert the angle of inclination or declination from degrees to radians if necessary.
- Calculate the tangent of the angle.
- Multiply the horizontal distance (L) by the tangent of the angle to get the vertical drop (D).
Table of General Terms and Calculations
To facilitate easier understanding and usage of the calculator, here’s a quick reference table:
| Term | Definition | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical Drop (D) | The drop in height vertically | D = L * tan(Angle) |
| Horizontal Distance (L) | The distance measured horizontally | Used in the formula |
| Angle of Inclination/Declination | The angle at which the incline/decline occurs | Must be converted to radians for calculations |
This table serves as a helpful guide for users who need to quickly refer to or explain the necessary terms and their roles in the calculations.
Example of Angle Drop Calculator
Consider a scenario where a civil engineer needs to calculate the vertical drop for a new ramp that extends 100 meters horizontally with an inclination angle of 5 degrees:
-
Convert the angle of 5 degrees to radians:
- Angle in Radians = 5 * (π / 180) ≈ 0.0873 radians.
-
Calculate the tangent of the angle:
- tan(5 degrees) ≈ 0.0875.
-
Calculate the vertical drop:
- D = 100 m * 0.0875 ≈ 8.75 meters.
This example demonstrates how the calculator can be effectively used in practical situations, such as construction and engineering projects.
Most Common FAQs
The Angle Drop Calculator is widely used in civil engineering, construction, landscaping, and any field that requires precise slope management.
The greater the angle of inclination, the greater the vertical drop for the same horizontal distance, making this calculator crucial for accurately planning inclined structures.
Yes, the calculator is design to handle all angles, but accuracy is crucial when measuring the angle and the horizontal distance, especially on steep slopes.