The Angle Dilation Calculator is an advanced tool used primarily in the fields of optics and physics. It assists scientists and engineers in determining how light bends or refracts when it passes from one medium into another with a different refractive index. This phenomenon is governed by Snell’s Law, which is crucial for designing optical instruments, understanding vision correction, and various applications in physics and engineering.
Formula of Angle Dilation Calculator
The fundamental formula used in the Angle Dilation Calculator is based on Snell’s Law, which relates the angles of incidence and refraction to the refractive indices of two different media:
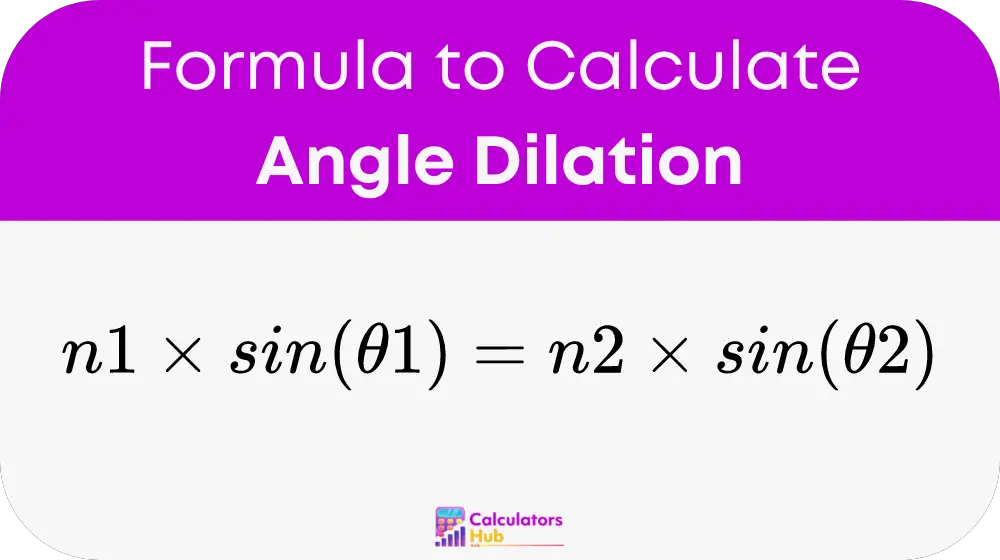
Where:
- n1 is the refractive index of the first medium.
- θ1 is the angle of incidence (the angle at which the incoming light strikes the surface).
- n2 is the refractive index of the second medium.
- θ2 is the angle of refraction (the angle at which the light travels in the second medium).
This formula allows for precise calculations of how light’s direction changes upon entering a new medium, which is essential for applications requiring precise optical alignments.
Table of Common Terms and Conversions
To aid in understanding and using the calculator more effectively, below is a table of common terms related to angle dilation and their relevance:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Refractive Index (n) | A measure of how much the speed of light is reduced inside a medium compared to vacuum. |
| Angle of Incidence (θ1) | The angle at which light rays strike a medium boundary. |
| Angle of Refraction (θ2) | The angle at which light rays enter the second medium. |
| Snell’s Law | A formula used to calculate the refraction of light between two media. |
This table provides a quick reference guide for users needing to understand or explain the concepts involved in angle dilation calculations.
Example of Angle Dilation Calculator
For instance, consider a scenario where light travels from air (refractive index = 1.0) into water (refractive index = 1.33). If the angle of incidence (θ1) is 30 degrees, the calculator would determine the angle of refraction (θ2) using Snell’s Law:
- Convert the angle of incidence to radians for calculation: θ1 = 30 degrees = π/6 radians.
- Apply Snell’s Law:
- sin(θ2) = (n1/n2) * sin(θ1)
- sin(θ2) = (1.0 / 1.33) * sin(π/6)
- θ2 ≈ 22 degrees
This example would show how light bends when entering water, which is useful for understanding phenomena like the apparent bending of a stick partially submerged in water.
Most Common FAQs
Understanding angle dilation is crucial for designing optical devices such as lenses and prisms. Ensuring they function correctly by precisely directing light paths.
< /div>The higher the difference between the refractive indices of the two media. The greater the angle dilation, meaning light bends more significantly.
Yes, the calculator works for any type of light, although the specific wavelength of the light can affect the refractive index slightly, primarily in dispersive media.