An Air Velocity Calculator is a critical tool used in various fields including HVAC (heating, ventilating, and air conditioning), environmental engineering, and industrial process control. This calculator assists professionals and technicians in measuring the speed at which air moves through different conduits such as ducts or pipes, which is vital for system design, efficiency analysis, and ensuring compliance with health and safety regulations.
Formula of Air Velocity Calculator
The calculation of air velocity can be approached using the continuity equation, which is a fundamental principle in fluid dynamics. The formula to calculate air velocity is:
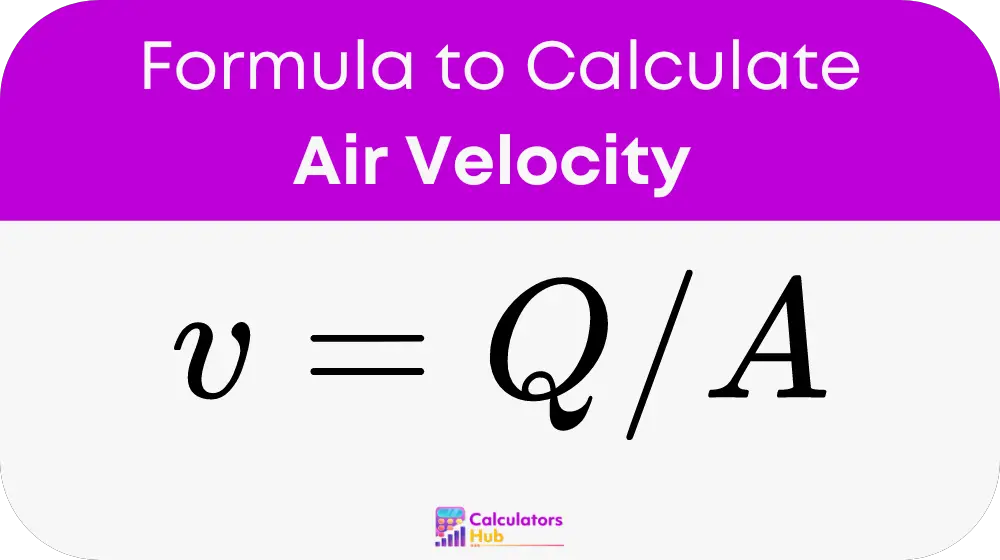
where:
- v is the air velocity (in meters per second or feet per second),
- Q is the volumetric flow rate (in cubic meters per second or cubic feet per minute),
- A is the cross-sectional area of the duct or pipe (in square meters or square feet).
Detailed Calculation Steps:
- Determine the volumetric flow rate (Q): This is the volume of air moving through a duct or pipe per unit of time.
- Determine the cross-sectional area (A):
- For a circular duct, calculate using the diameter (d) of the duct: A = π * (d / 2)^2
- For a rectangular duct, calculate using the width (w) and height (h) of the duct: A = w * h
- Calculate the air velocity (v): Using the formula v = Q / A, determine the velocity at which air is moving through the duct.
Table for General Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Air Velocity (v) | Speed at which air is moving, measured in m/s or ft/s |
| Volumetric Flow Rate (Q) | Volume of air flowing per unit time, measured in m³/s or cfm |
| Cross-Sectional Area (A) | Area through which air is flowing, measured in m² or ft² |
| Diameter (d) | For circular ducts, the distance across the duct |
| Width (w) | For rectangular ducts, the side-to-side measurement |
| Height (h) | For rectangular ducts, the top-to-bottom measurement |
Example of Air Velocity Calculator
Consider an HVAC system where the duct has a circular cross-section with a diameter of 0.5 meters. If the volumetric flow rate of air through the duct is 2 cubic meters per second, calculate the air velocity:
- Calculate the cross-sectional area (A): A = π * (0.5 / 2)^2 = 0.196 m²
- Calculate the air velocity (v): v = 2 / 0.196 ≈ 10.2 m/s
Therefore, the air velocity through the duct is approximately 10.2 meters per second.
Most Common FAQs
A1: Proper air velocity ensures efficient air distribution, enhances comfort levels, and prevents system strain, leading to energy efficiency and prolonged system life.
A2: Yes, calculating air velocity helps in ensuring that ventilation systems in workplaces meet health and safety standards by preventing the buildup of harmful pollutants.
A3: In large settings, variations in duct size, complex flow patterns, and environmental factors can complicate accurate measurement, requiring careful calibration and sometimes multiple measurements.