The Air Flow Coefficient Calculator is a pivotal tool used by engineers and HVAC specialists to determine the flow capacity of valves and other components within air handling systems. By calculating the coefficient, also known as Cv, professionals can ensure that components are properly sized and optimized for the required flow rate, minimizing energy consumption and enhancing overall system performance.
Formula of Air Flow Coefficient Calculator
The formula for calculating the air flow coefficient (Cv) provides a measure of how much flow can pass through a valve or fitting with a given pressure drop and is defined as:
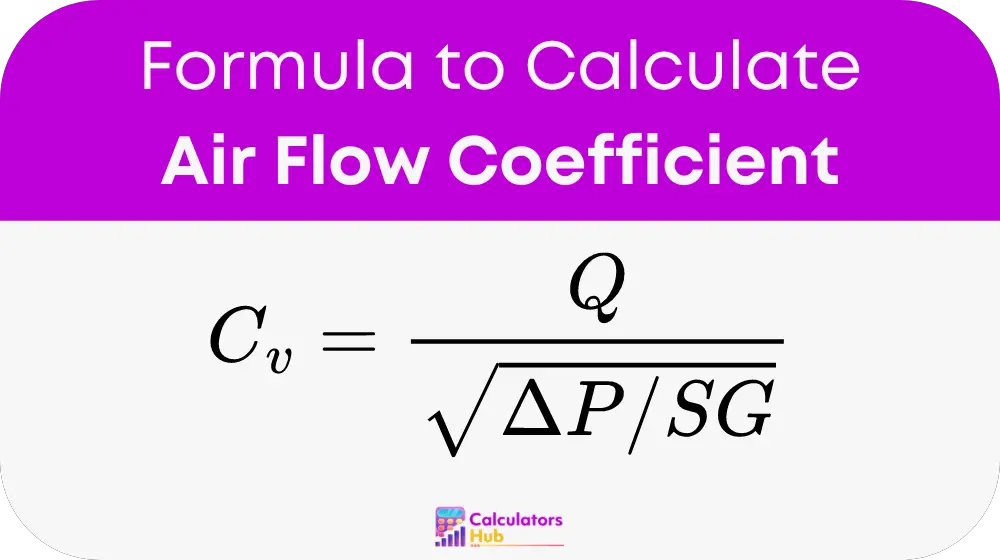
Parameters Explained:
- Q (Volumetric Flow Rate): The amount of air flowing through the component, measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM) or cubic meters per second (m³/s).
- Delta P (Pressure Drop): The difference in pressure across the component, measured in pounds per square inch (psi) or Pascals (Pa).
- SG (Specific Gravity): The ratio of the density of the fluid (air in this case) to the density of water. For air, the specific gravity is approximately 1.
This formula helps in sizing equipment within air distribution systems by providing a clear indication of how different components will perform under various conditions.
General Terms Table
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Air Flow Coefficient (Cv) | A dimensionless number that indicates the flow capacity of a valve or orifice at a given pressure drop. |
| Volumetric Flow Rate (Q) | The volume of air passing through a component per unit of time. |
| Pressure Drop (Delta P) | The reduction in pressure from one side of a component to the other, caused by resistance to flow. |
| Specific Gravity (SG) | A dimensionless number that represents the ratio of the density of a fluid compared to the density of water. |
Example of Air Flow Coefficient Calculator
For example, if an engineer needs to determine the Cv for a valve where the air flow rate is 200 CFM. The pressure drop is 2 psi, and the air’s specific gravity is approximately 1, the calculation would be:
- Cv = 200 / sqrt(2 / 1) = 200 / 1.414 = 141.42
This result indicates that the valve has a flow coefficient of 141.42. Which can be used to compare with manufacturer specifications to ensure it meets the system’s requirements.
Most Common FAQs
The air flow coefficient is crucial for determining the appropriate sizing of components. To ensure efficient operation without excessive energy use or undue strain on the system.
Higher pressure drops can lead to increased energy consumption as the system has to work harder to maintain the desired flow rate. Affecting both performance and operational costs.
Yes, Cv can change due to wear and tear or buildup within the valve. Which may alter flow characteristics and system efficiency, highlighting the need for regular maintenance and monitoring.