The Acceleration With Two Masses Calculator is designed to determine the acceleration of a system involving two masses connected by a pulley. This calculation is essential for understanding basic principles in mechanics, such as Newton's Second Law of Motion, and has practical applications in areas ranging from engineering to education.
Formula of Acceleration With Two Masses Calculator
The key to using the Acceleration With Two Masses Calculator effectively lies in the formula:
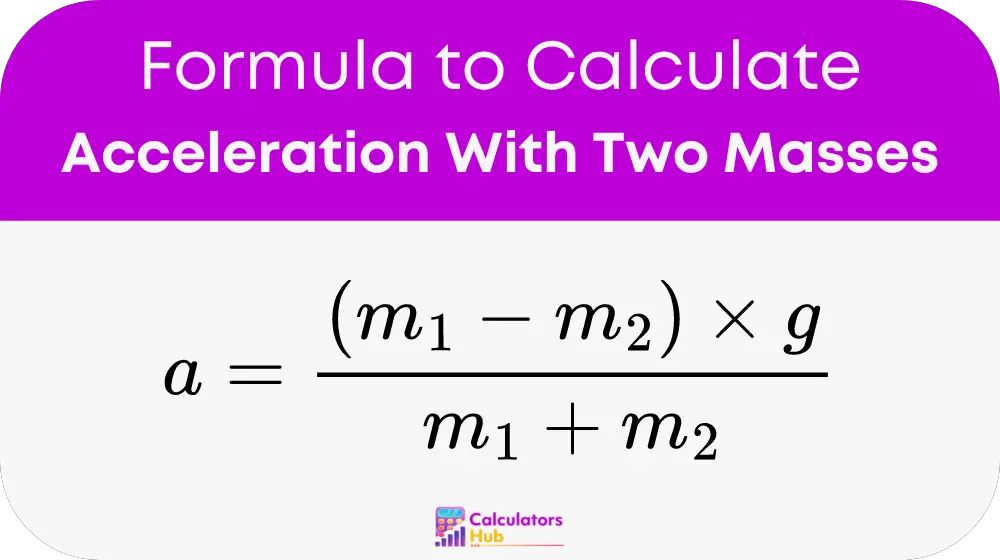
Here, a represents the acceleration of the system, m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects, and g is the acceleration due to gravity, approximately 9.81 m/s². This formula helps clarify how different mass ratios affect the acceleration of the entire system.
General Table of Common Calculations
To aid users, here's a table with pre-calculated values showing how different combinations of masses affect acceleration:
| m1 (kg) | m2 (kg) | Acceleration (m/s²) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3.27 |
| 2 | 3 | 2.45 |
| 5 | 10 | 4.90 |
This table serves as a quick reference to understand typical outcomes without performing manual calculations each time.
Example of Acceleration With Two Masses Calculator
Consider a scenario where m1 is 1 kg and m2 is 3 kg. Using our formula:
a = (3 - 1) * 9.81 / (1 + 3) = 5.86 m/s²
This calculation illustrates how the Acceleration With Two Masses Calculator simplifies complex calculations into understandable results.
Most Common FAQs
A: The difference in mass between the two objects significantly influences the acceleration. Greater differences result in higher acceleration.
A: Yes, as long as the system consists of two masses and gravity is the only force acting on them.
A: This calculator is used in designing systems like elevators and cable cars, where understanding the interaction between different weights is crucial.