The AC Motor Torque Calculator determines the torque produced by an AC motor. Torque is a measure of the rotational force the motor generates. This calculation is crucial for designing motor systems, ensuring they can handle the required loads. By using this calculator, you can quickly find the torque without manual calculations, saving time and reducing errors.
Formula of AC Motor Torque Calculator
The torque (T) of an AC motor can be calculated using the following formula:
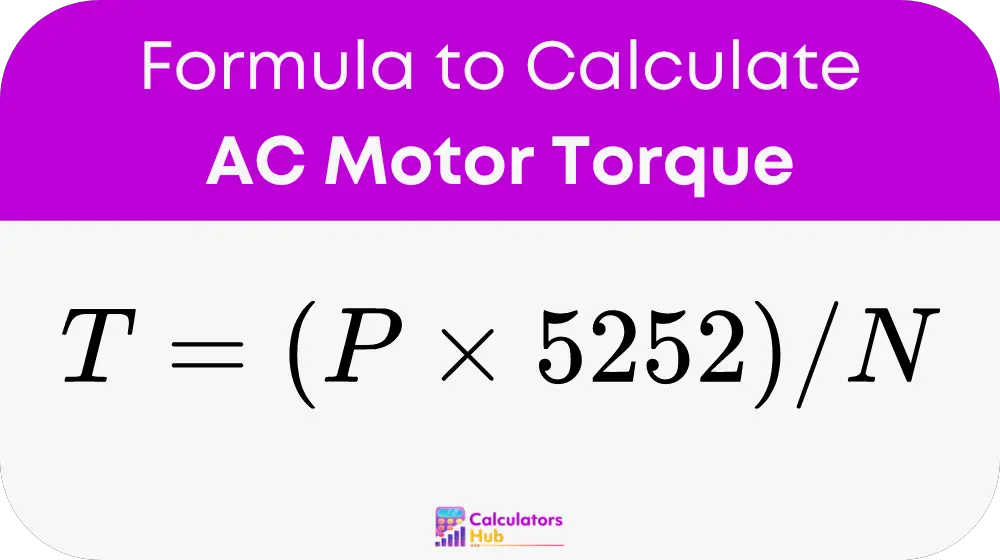
where:
- T is the torque in pound-feet (lb-ft)
- P is the power in horsepower (hp)
- N is the speed in revolutions per minute (RPM)
This formula helps you find the torque by knowing the power and speed of the motor.
Conversion Table
Below is a table of common values that people search for. This table provides quick references for torque calculations without needing to calculate each time.
| Power (hp) | Speed (RPM) | Torque (lb-ft) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1800 | 2.92 |
| 5 | 1800 | 14.6 |
| 10 | 1800 | 29.2 |
| 15 | 1800 | 43.8 |
| 20 | 1800 | 58.4 |
You can use this table to quickly find the torque for common power and speed values.
Example of AC Motor Torque Calculator
Let's go through an example to see how the formula works.
Suppose you have an AC motor with a power of 10 horsepower and a speed of 1800 RPM. Using the formula:
T = (P * 5252) / N T = (10 * 5252) / 1800 T = 29.2 lb-ft
So, the torque produced by this motor is 29.2 pound-feet.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Torque is the measure of rotational force produced by the motor. It is essential for determining how much load the motor can handle.
Knowing the torque helps in designing and selecting the right motor for specific applications. It ensures the motor can handle the required load without failure.
This calculator is specifically for AC motors. Different types of motors may require different formulas for accurate torque calculation.