The RCF to RPM calculator is a handy tool used in various fields such as biology, chemistry, and medicine to convert Rotational Centrifugal Force (RCF) into Revolutions Per Minute (RPM) and vice versa. This conversion is crucial for researchers, laboratory technicians, and professionals working with centrifuges, as it helps in understanding the speed at which particles separate in a centrifugal field.
Formula of RCF to RPM Calculator
The calculation performed by the RCF to RPM calculator follows a simple yet essential formula:
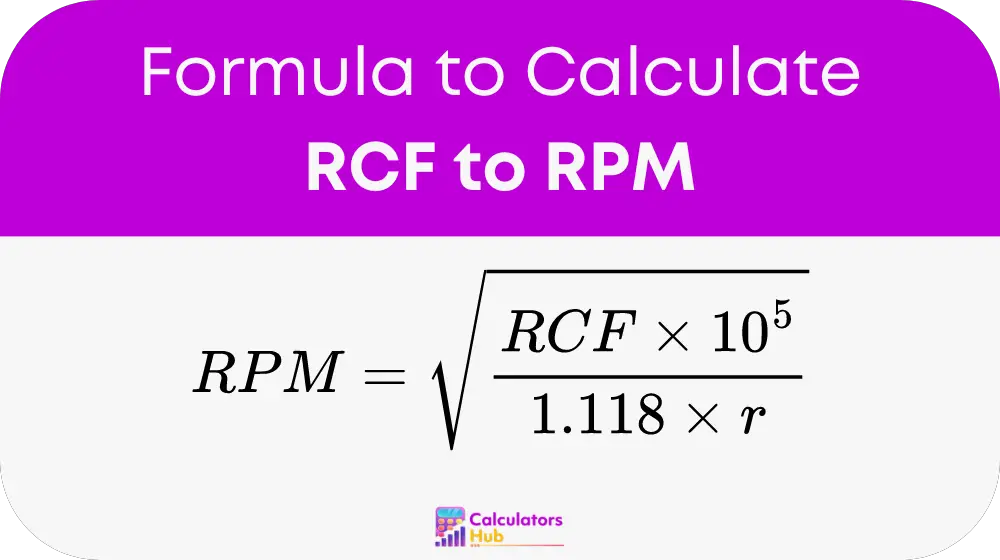
Where:
- RPM stands for revolutions per minute, indicating the speed at which the centrifuge rotor spins.
- RCF represents the Rotational Centrifugal Force, measured in 'g' (times the acceleration due to gravity).
- r denotes the radius of the rotor in centimeters.
General Terms Table
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Rotational Centrifugal Force (RCF) | The force experienced by an object rotating in a centrifuge. |
| Revolutions Per Minute (RPM) | The number of complete rotations that occur in one minute. |
| Radius of the Rotor (r) | The distance from the center to the outer edge of the centrifuge rotor. |
This table provides a quick reference for general terms related to centrifugation, aiding users in understanding the concepts without the need for constant calculations.
Example of RCF to RPM Calculator
Let's illustrate the usage of the RCF to RPM calculator with an example:
Suppose we have an RCF of 1000 g and a rotor radius of 10 centimeters. Plugging these values into the formula:
RPM = √(1000 × 10^5 / 1.118 × 10)
≈ √(100000000 / 11.18)
≈ √(8950.34) ≈ 94.59 RPM
So, with an RCF of 1000 g and a rotor radius of 10 cm, the RPM would be approximately 94.59.
Most Common FAQs
RCF, or Rotational Centrifugal Force, determines the sedimentation rate of particles in a centrifuge. It influences the separation of components based on their density, size, and shape.
The rotor radius directly impacts the magnitude of centrifugal force exerted on the samples. A larger rotor radius results in higher RCF and faster sedimentation rates, while a smaller radius produces lower RCF and slower separations.