The Clutch Heat Generation Calculator estimates the amount of heat produced when a clutch engages. This is vital in assessing clutch performance, preventing overheating, and ensuring efficient energy transfer in automotive and industrial systems.
By using this calculator, engineers can evaluate the thermal load on a clutch, optimize its design, and choose materials that handle the generated heat effectively. It is especially useful in scenarios involving frequent clutch engagements, such as in heavy machinery or high-performance vehicles.
Formula of Clutch Heat Generation Calculator
The heat generated by the clutch is calculated as:
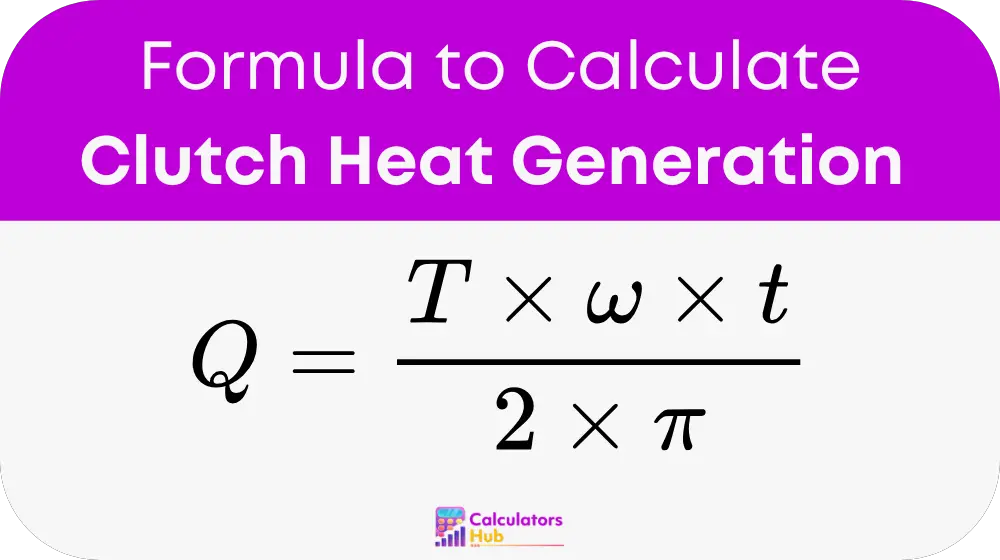
Where:
Q = Heat generated (Joules).
T = Torque applied to the clutch (Newton-meters).
ω = Rotational speed of the clutch (radians per second).
t = Engagement time of the clutch (seconds).
Steps to Calculate Clutch Heat Generation
- Determine Torque (T):
Measure the torque applied to the clutch in Newton-meters. This can be done using a torque wrench or calculated from the engine’s power and speed. - Determine Rotational Speed (ω):
- Measure the rotational speed of the clutch in revolutions per minute (RPM).
- Convert RPM to radians per second using:
ω = (RPM × 2 × π) / 60
- Determine Engagement Time (t):
Measure the time taken for the clutch to fully engage in seconds. - Calculate Heat Generation (Q):
Substitute the values of T, ω, and t into the formula to calculate Q.
Reference Table for Common Values
| Torque (T) (Nm) | Rotational Speed (RPM) | Engagement Time (t) (s) | Heat Generated (Q) (J) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 1000 | 2 | 523.6 |
| 100 | 1500 | 1.5 | 1570.8 |
| 75 | 1200 | 3 | 2261.95 |
This table provides quick reference values to save time in common scenarios.
Example of Clutch Heat Generation Calculator
Scenario
A clutch operates with the following parameters:
- Torque (T) = 80 Nm
- Rotational speed (RPM) = 1200
- Engagement time (t) = 2 seconds
Step 1: Convert RPM to radians per second
ω = (1200 × 2 × π) / 60 = 125.66 radians/second
Step 2: Calculate heat generated
Using the formula:
Q = (80 × 125.66 × 2) / (2 × π)
Q = 3200 / 6.2832 ≈ 509.3 Joules
Final Result
The clutch generates approximately 509.3 Joules of heat during engagement.
Most Common FAQs
Calculating clutch heat helps in designing durable systems, choosing appropriate materials, and avoiding issues like overheating or wear during operation.
Reducing engagement time, optimizing torque transmission, or using advanced friction materials can minimize heat buildup.
Excessive heat can lead to clutch failure, reduced efficiency, or damage to adjacent components. Regular maintenance and design adjustments can prevent this.