The Bike Leverage Ratio Calculator is a valuable tool for cyclists, particularly those interested in optimizing their suspension setup. The leverage ratio describes how much the rear wheel of a bike moves in response to the movement of the suspension shock. This ratio is crucial for understanding and adjusting the suspension dynamics of a bike, which can significantly impact ride quality, performance, and comfort. By using this calculator, riders can fine-tune their bike's suspension to better suit their riding style and terrain.
Formula of Bike Leverage Ratio Calculator
The formula to calculate the leverage ratio is straightforward:
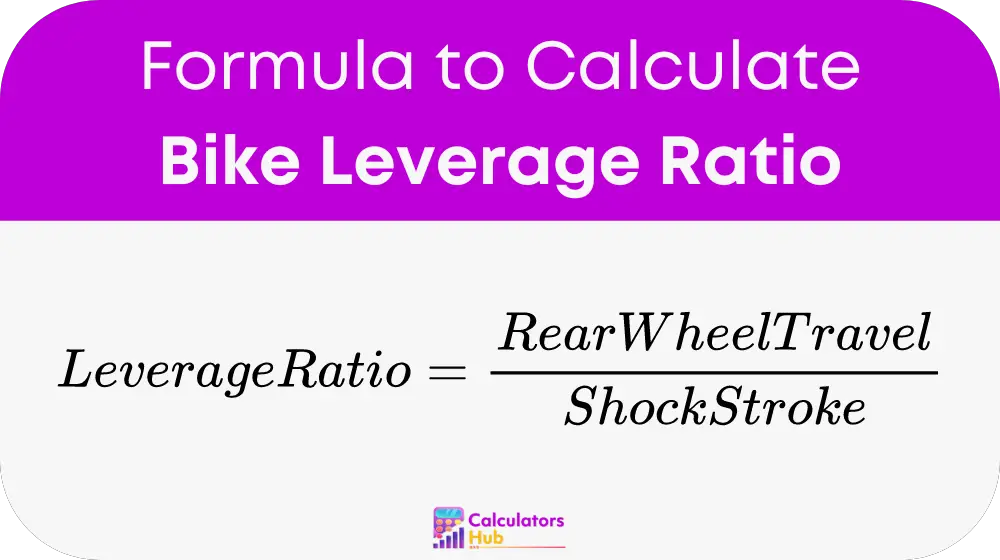
Where:
- Rear Wheel Travel: The total vertical movement of the rear wheel when the suspension is fully compressed, typically measured in millimeters or inches.
- Shock Stroke: The total movement of the suspension shock (the damper) itself, also measured in millimeters or inches.
This formula allows riders to understand how much the rear wheel moves for every unit of shock movement. A higher leverage ratio typically indicates a softer suspension, while a lower ratio indicates a stiffer setup.
General Reference Values for Bike Leverage Ratio Calculation
To assist with quick calculations, here’s a table that provides reference values for common terms and their typical ranges. These can help you estimate the leverage ratio for different suspension setups without needing to calculate each time.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Rear Wheel Travel | The total movement of the rear wheel, usually between 100mm to 200mm for most mountain bikes. |
| Shock Stroke | The total movement of the shock, typically ranging from 30mm to 75mm. |
| Common Leverage Ratios | Most bikes have a leverage ratio between 2.0 and 3.5. |
These reference values can guide you in quickly estimating the leverage ratio based on your bike's specifications.
Example of Bike Leverage Ratio Calculator
Let’s go through an example to see how the Bike Leverage Ratio Calculator works in practice.
Imagine you have a mountain bike with a rear wheel travel of 150mm and a shock stroke of 50mm. Using the leverage ratio formula:
Leverage Ratio = 150mm / 50mm = 3.0
This means that for every millimeter of movement in the shock, the rear wheel moves 3 millimeters. A leverage ratio of 3.0 is typical for many full-suspension mountain bikes, providing a balance between plushness and responsiveness.
Most Common FAQs
The leverage ratio determines how sensitive the rear suspension is to impacts and terrain changes. A higher leverage ratio makes the suspension feel softer, which can improve comfort but might reduce pedaling efficiency. Conversely, a lower leverage ratio results in a stiffer suspension, which can enhance pedaling efficiency but may decrease comfort on rough terrain.
Changing the leverage ratio typically involves altering the suspension components, such as installing a shock with a different stroke length or adjusting the linkage. However, it's essential to consult with a professional or refer to your bike's specifications to ensure compatibility and maintain safe handling characteristics.
A higher leverage ratio generally makes a bike more compliant over rough terrain, improving traction and comfort. However, it may also cause the bike to bottom out more easily. A lower leverage ratio makes the suspension firmer, which can improve stability and control during aggressive riding, but it may also transmit more trail feedback to the rider.