The Aerodynamic Power Calculator is a vital tool for engineers, designers, and enthusiasts in fields such as automotive, aeronautics, and cycling. It helps calculate the power required to overcome aerodynamic drag when an object moves through the air. This calculation is crucial for optimizing designs to improve performance and efficiency in vehicles, aircraft, and sports equipment.
Formula of Aerodynamic Power Calculator
Aerodynamic Power Calculation:
The formula to calculate aerodynamic power is given by:
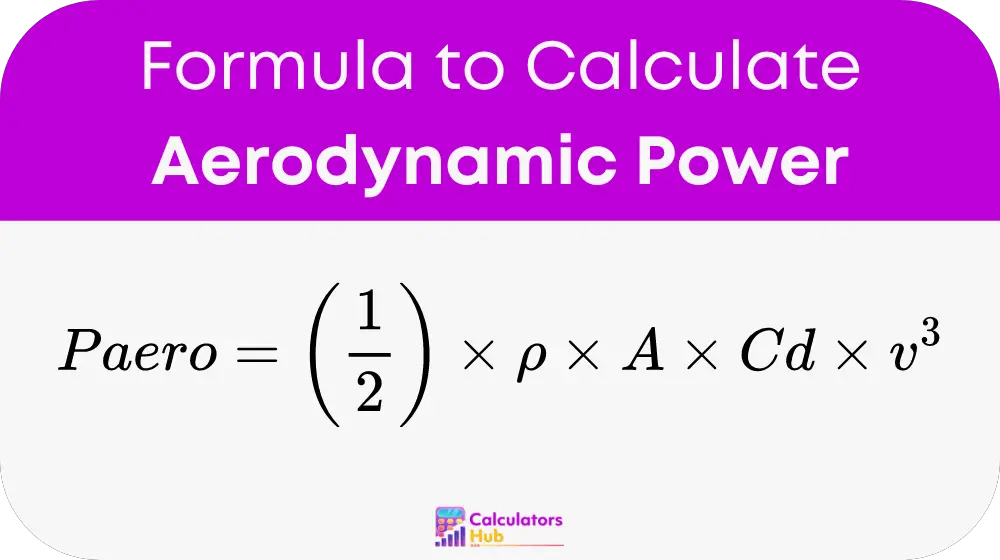
Where:
- Paero: Aerodynamic power in Watts
- rho: Air density in kg/m^3
- A: Frontal area in m^2
- Cd: Drag coefficient, a dimensionless number
- v: Velocity in m/s
Detailed Explanation:
- Air Density (rho):
- The mass per unit volume of the air, typically about 1.225 kg/m^3 at sea level under standard conditions. This factor can vary based on altitude and temperature.
- Frontal Area (A):
- The area of the object facing the direction of motion which directly interacts with the airflow, like the front of a car or a bicycle.
- Drag Coefficient (Cd):
- A dimensionless number that quantifies the drag resistance of an object in a fluid environment. It is influenced by the shape of the object and the flow of air around it.
- Velocity (v):
- The speed of the object relative to the air. Aerodynamic drag, and consequently the power needed to overcome it, dramatically increases with the cube of the velocity.
Table for General Terms and Quick Calculations
To facilitate understanding, here’s a table that outlines general terms and provides example calculations:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Aerodynamic Power (Paero) | Power required to overcome aerodynamic drag, measured in Watts. |
| Air Density (rho) | The density of air, usually measured in kg/m³. |
| Frontal Area (A) | The area of the front of the object facing the airflow, measured in m². |
| Drag Coefficient (Cd) | Dimensionless number representing the object's resistance to air flow. |
| Velocity (v) | Speed of the object relative to the air, measured in m/s. |
Example Calculations:
| rho (kg/m³) | A (m²) | Cd | v (m/s) | Paero (Watts) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.225 | 2.5 | 0.3 | 15 | 981.6 |
| 1.225 | 1.2 | 0.29 | 20 | 1066.6 |
| 1.225 | 1.8 | 0.28 | 25 | 2227.8 |
Example of Aerodynamic Power Calculator
Consider a scenario where a car with a frontal area of 2.2 m², a drag coefficient of 0.28, and traveling at a speed of 30 m/s through standard sea-level air:
- Paero = (1/2) * 1.225 * 2.2 * 0.28 * (30^3)
- Paero = 1846 Watts
This calculation shows the power required to overcome the aerodynamic drag under these specific conditions.
Most Common FAQs
A1: Reducing drag allows a vehicle to operate with less energy for the same speed, significantly enhancing fuel efficiency and performance.
A2: Yes, optimizing the shape and surface texture of the vehicle, adding aerodynamic aids like spoilers, and reducing frontal area can effectively lower the drag coefficient.
A3: Absolutely. This calculator is versatile and can be adapted for any object moving through air, including UAVs, by accurately inputting the specific parameters.