The Standard to General Form Calculator transforms the standard form of a circle’s equation, (x – h)^2 + (y – k)^2 = r^2, where (h, k) is the center and r is the radius, into its more general counterpart. This conversion is particularly useful in analytical geometry, where simplifying circle equations helps in sketching circles and solving complex geometry problems.
Formula of Standard to General Form Calculator
To convert the standard form to the general form, follow these detailed steps:
Begin with the standard form:
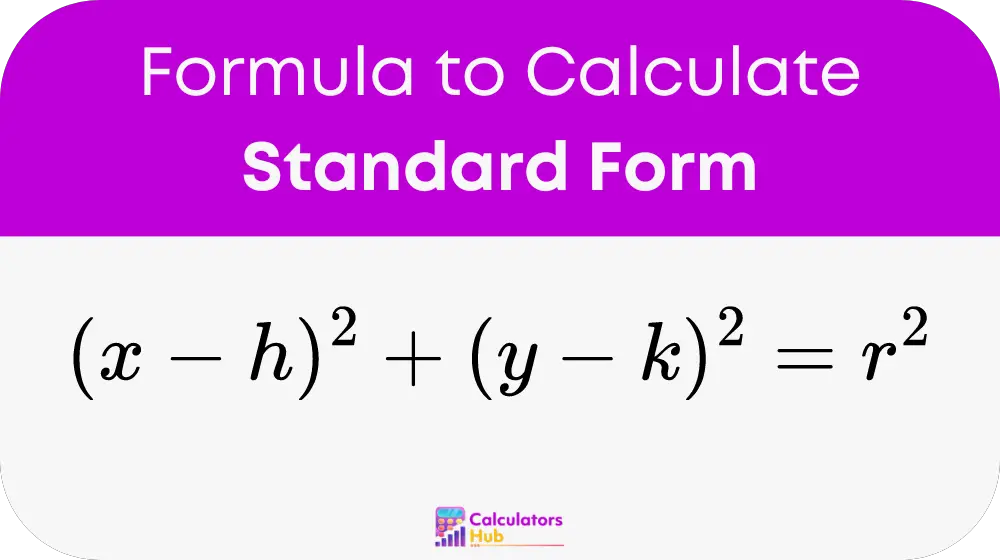
Expand and simplify: x^2 – 2hx + h^2 + y^2 – 2ky + k^2 = r^2 x^2 + y^2 – 2hx – 2ky + (h^2 + k^2 – r^2) = 0
The resulting general form is: x^2 + y^2 + Ax + By + C = 0 Where A = -2h, B = -2k, and C = h^2 + k^2 – r^2.
This formula not only facilitates easier handling of circle equations but also forms the foundation for further geometric explorations.
Table of General Terms
Here is a quick reference table that users can consult without performing calculations each time:
| Term | Standard Form Representation | General Form Conversion |
|---|---|---|
| Center of Circle (h, k) | h, k in (x – h)^2 + (y – k)^2 = r^2 | Affects A and B in x^2 + y^2 + Ax + By + C = 0 |
| Radius r | r in (x – h)^2 + (y – k)^2 = r^2 | Determines C |
| Coefficients A, B, C | Derived from h, k, r | Directly used in general form equation |
Example of Standard to General Form Calculator
Consider converting the standard form equation (x – 3)^2 + (y + 4)^2 = 16 into general form:
- Standard Form: (x – 3)^2 + (y + 4)^2 = 16
- Expanding and Simplifying: x^2 – 6x + 9 + y^2 + 8y + 16 = 16 x^2 + y^2 – 6x + 8y + 9 = 0
- General Form: x^2 + y^2 – 6x + 8y + 9 = 0
This example illustrates the conversion process clearly and shows the ease with which the calculator can be used to simplify equations.
Most Common FAQs
A1: Standard form specifically denotes a circle centered at (h, k) with radius r and appears as (x – h)^2 + (y – k)^2 = r^2. General form simplifies this to x^2 + y^2 + Ax + By + C = 0, which is easier to use in most algebraic operations.
A2: From the standard form equation, A = -2h, B = -2k, and C = h^2 + k^2 – r^2. Calculated by expanding and rearranging the equation.
A3: While this tool is designed for circles, similar concepts apply to ellipses and hyperbolas. Though separate calculators are recommended for those due to different standard forms.