–
A Cross Ratio Calculator helps determine the cross ratio of four collinear points, a fundamental concept in projective geometry and mathematical analysis. The cross ratio (CR) is used to measure how four points divide a line segment, which is important in various applications, including perspective transformations, image processing, and optical geometry.
The cross ratio remains invariant under projective transformations, making it a valuable tool in geometry and computer vision. By using this calculator, users can quickly compute the cross ratio without manually solving the mathematical formula.
Formula of Cross Ratio Calculator
The formula to calculate the cross ratio (CR) of four collinear points A, B, C, D is:
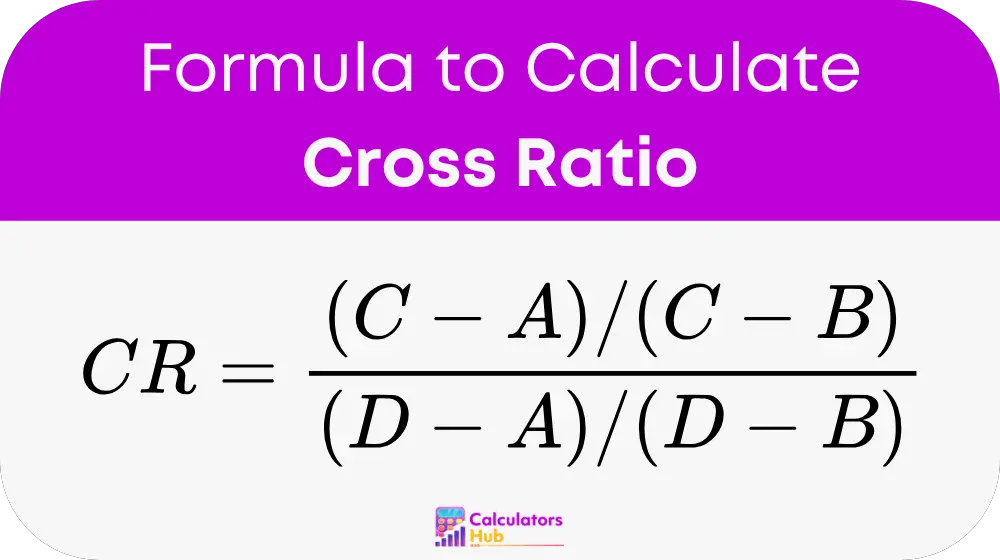
Where:
- A, B, C, D are four collinear points on a straight line.
- CR is the cross ratio, a dimensionless quantity that remains invariant under projective transformations.
The cross ratio is widely used in geometry and physics because of its consistency in different perspectives.
Pre-Calculated Cross Ratio Table
For quick reference, here are some common cross-ratio values for specific point placements:
| Points (A, B, C, D) | Cross Ratio (CR) |
|---|---|
| (1, 2, 3, 4) | 1 |
| (2, 4, 6, 8) | 1 |
| (1, 3, 5, 7) | 1 |
| (1, 2, 4, 8) | 2 |
| (1, 4, 2, 8) | 0.5 |
This table provides a quick way to check common values without recalculating each time.
Example of Cross Ratio Calculator
Let’s calculate the cross ratio for the points A = 2, B = 4, C = 6, and D = 8.
- Using the formula:CR = ((6 – 2) / (6 – 4)) / ((8 – 2) / (8 – 4))
- Simplifying:CR = (4 / 2) / (6 / 4)
CR = 2 / 1.5
CR = 1.33
Thus, the cross ratio for these four points is 1.33.
Most Common FAQs
The cross ratio is crucial in projective geometry and computer vision because it remains constant under transformations. It helps in applications like 3D reconstruction and perspective corrections.
Yes, depending on the order of the points, the cross ratio can be negative, which indicates different segment divisions.
The cross ratio is used in mathematics, physics, photography, and architecture to analyze perspective, geometric invariants, and optical transformations.