The Clog2 Calculator is an essential tool that computes the ceiling of the base-2 logarithm of a given number. This calculation is pivotal in various fields, particularly in computer science, where it aids in tasks such as determining the minimum number of bits required to represent a number in binary.
Formula of Clog2 Calculator
The formula for the ceiling of the base-2 logarithm, clog2(x), is expressed as:
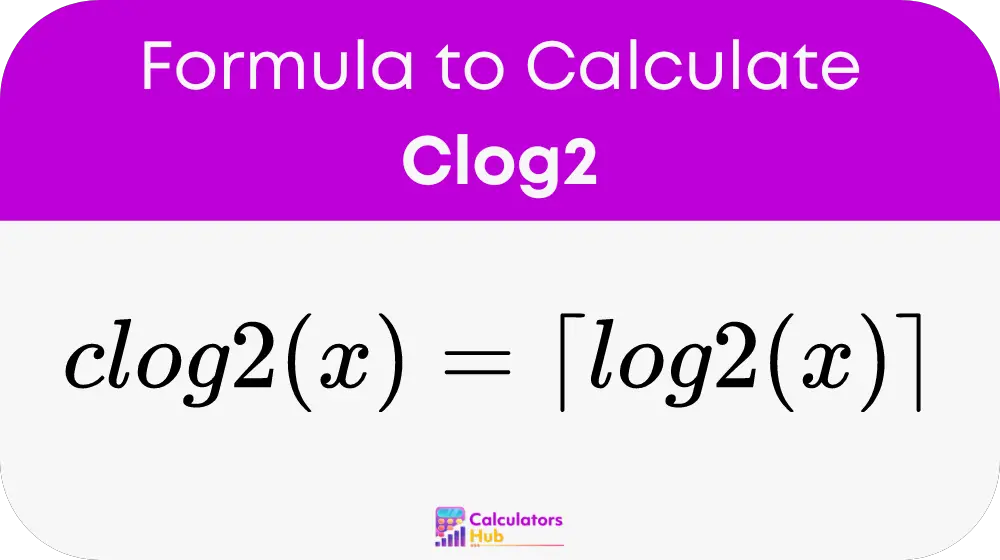
Here, log2(x) represents the base-2 logarithm of x, and the ceiling() function rounds this logarithm up to the nearest integer. This ensures that the output is always an integer, even if log2(x) results in a fractional value.
Steps to Calculate Clog2
To effectively use the Clog2 Calculator, follow these steps:
- Calculate the base-2 logarithm: Begin by computing
log2(x)for your input valuex. - Apply the ceiling function: Next, round the result of
log2(x)up to the nearest integer using the ceiling function. This gives you the clog2 value.
Table of General Terms
The following table includes pre-calculated clog2 values for commonly used numbers:
| Input (x) | log2(x) | clog2(x) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 1.58496 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 | 2 |
| 5 | 2.32193 | 3 |
| ... | ... | ... |
This table can be extremely helpful for quick reference without the need for manual calculations.
Example of Clog2 Calculator
For an input of 5:
- Calculate log2(5) which approximately equals 2.32193.
- Applying the ceiling function, we round 2.32193 up to the nearest whole number, which is 3.
Thus, clog2(5) = 3.
Most Common FAQs
Clog2 is widely used in computing to determine the number of bits required for binary representation of numbers, optimizing memory allocation.
No, clog2 calculations are only valid for positive integers. Negative inputs do not yield valid logarithmic values.
The Clog2 Calculator is highly accurate, providing exact ceiling values for any positive integer input.