The Anchor Swing Circle Calculator is an essential tool for sailors and mariners. It calculates the area needed around an anchored boat to ensure it does not collide with other objects or boats as it swings around the anchor due to wind or current. This calculation is crucial for safe anchoring, particularly in crowded or confined waters.
Formula of Anchor Swing Circle Calculator
To determine the swing circle radius of an anchored vessel, you need to take into account the following:
- Length of the Anchor Rode (L): This is the total length of the chain or rope that extends from the boat to the anchor on the seabed. It’s usually measured in meters (m) or feet (ft).
- Length of the Boat (B): The overall length of the boat, which also contributes to the swing radius.
The formula to calculate the radius of the swing circle is:
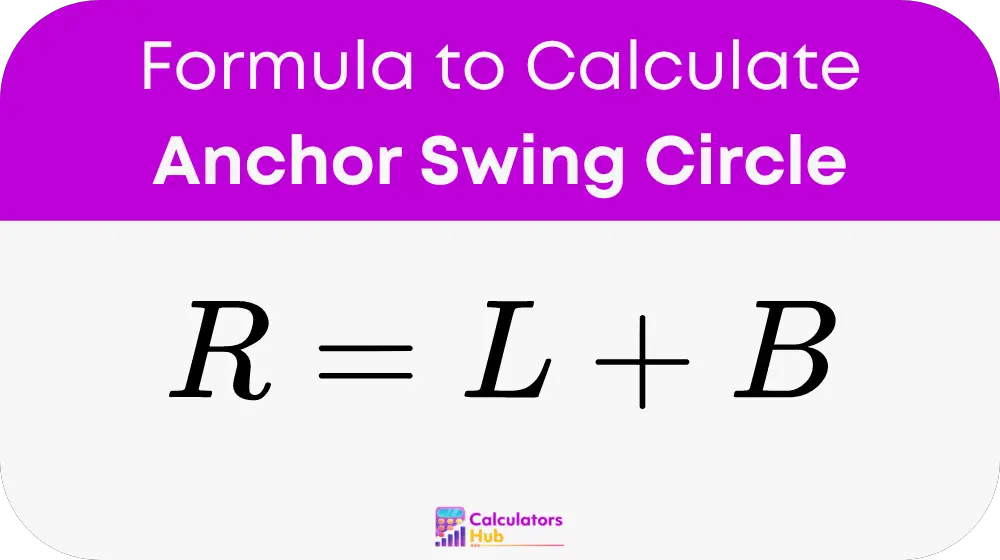
Where:
- R is the radius of the swing circle in meters (m) or feet (ft).
- L is the length of the anchor rode in meters (m) or feet (ft).
- B is the length of the boat in meters (m) or feet (ft).
This simple calculation ensures that the swing circle is sufficient to prevent the boat from encroaching on nearby boats or obstacles.
Table of Typical Swing Circles
Below is a table that provides examples of swing circles based on common lengths of anchor rode and boat sizes, making it easier for users to estimate their needs without individual calculations:
| Anchor Rode Length (L) | Boat Length (B) | Total Swing Circle Radius (R) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 m | 5 m | 15 m |
| 20 m | 10 m | 30 m |
| 30 m | 15 m | 45 m |
| 50 m | 20 m | 70 m |
This table helps to quickly visualize the space needed for safe anchoring based on different boat and rode lengths.
Example of Anchor Swing Circle Calculator
For instance, if a sailor is using a 40-meter anchor rode and their boat is 10 meters in length, the swing circle radius can be calculated as follows:
- Anchor Rode Length (L) = 40 m
- Boat Length (B) = 10 m
- Swing Circle Radius (R) = L + B = 40 m + 10 m = 50 m
This means the boat needs a clear radius of 50 meters around the anchor to swing safely without risk of collision.
Most Common FAQs
Factors such as tide, wind strength, and current direction can affect the actual swing radius. Mariners should consider these environmental factors when planning where to anchor.
Seabed composition (mud, sand, rock) can affect anchor hold and potentially the tightness of the swing circle. A secure anchor hold might reduce the radius as the boat will swing less with less rode slack.
It’s generally recommended to maintain at least twice the calculated swing circle radius from other nearby objects or boats to account for potential errors and environmental factors.