The Effective Thermal Resistance Calculator helps you determine how well a structure or material system resists the flow of heat. This tool is especially important in thermal engineering, insulation design, building construction, and electronics cooling.
When a wall, device, or system has multiple layers—each made of different materials—the calculator combines their individual thermal resistances into one total value. This total resistance tells you how effective the entire system is at resisting heat flow.
This tool is categorized under thermal and insulation performance calculators and is used in both engineering and real-world design applications.
formula
For Layers in Series (Heat Flow Perpendicular to Layers):
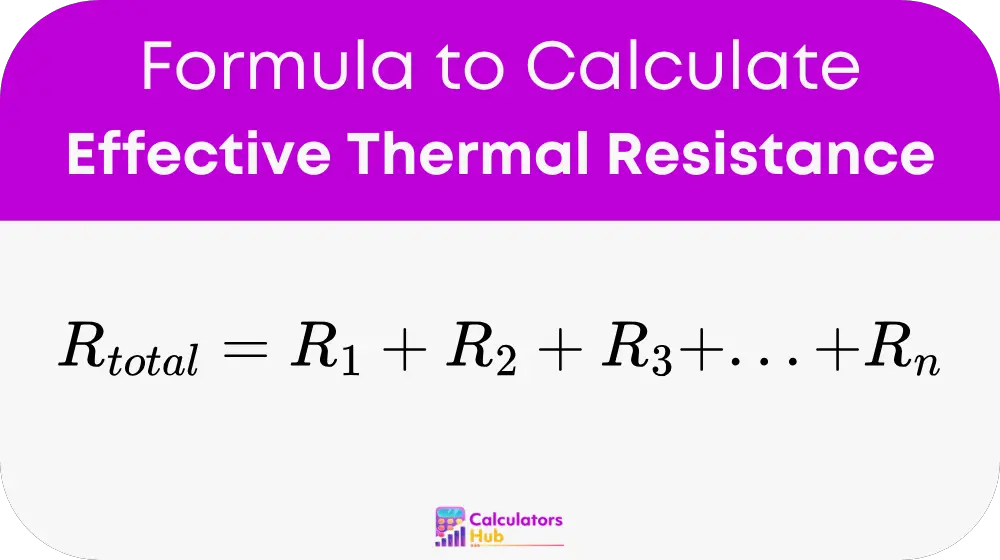
Where:
- R_total = Total Effective Thermal Resistance (units: m²·K/W, ft²·°F·hr/Btu, or similar)
- R_i = Thermal Resistance of the i-th layer or component
- R_i is calculated as: R_i = L_i / (k_i * A_i)
And:
- L_i = Thickness of the i-th layer (units: m, ft)
- k_i = Thermal Conductivity of the material in the i-th layer (units: W/m·K, Btu/hr·ft·°F)
- A_i = Area of the i-th layer perpendicular to heat flow (units: m², ft²)
Note: If A_i is the same across all layers, it can be factored out. In such cases, thermal resistance is often calculated per unit area.
This formula is used for systems where heat flows perpendicular to the surfaces of each material layer (common in walls, roofs, and multi-layer boards).
General Terms Table for Quick Reference
| Term | Description | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| R_total | Total thermal resistance of all layers combined | Used in thermal modeling |
| R_i | Thermal resistance of a single layer | Layer-specific performance |
| L_i | Thickness of a material layer | Insulation, wall thickness |
| k_i | Thermal conductivity of the material | Describes material’s ability to conduct heat |
| A_i | Surface area through which heat flows | Required when areas differ across layers |
| m²·K/W | SI unit for thermal resistance | Metric building applications |
| ft²·°F·hr/Btu | Imperial unit for thermal resistance | U.S. building insulation ratings |
Example
Let’s calculate the total thermal resistance of a wall made of three layers:
- Layer 1:
- Material: Brick
- Thickness (L_1) = 0.1 m
- Thermal conductivity (k_1) = 0.6 W/m·K
- Area (A_1) = 10 m²
- Layer 2:
- Material: Insulation foam
- Thickness (L_2) = 0.05 m
- Thermal conductivity (k_2) = 0.03 W/m·K
- Area (A_2) = 10 m²
- Layer 3:
- Material: Wood panel
- Thickness (L_3) = 0.02 m
- Thermal conductivity (k_3) = 0.12 W/m·K
- Area (A_3) = 10 m²
Step 1: Calculate R_i for each layer
R_1 = 0.1 / (0.6 × 10) = 0.0167 m²·K/W
R_2 = 0.05 / (0.03 × 10) = 0.1667 m²·K/W
R_3 = 0.02 / (0.12 × 10) = 0.0167 m²·K/W
Step 2: Add all R values
R_total = 0.0167 + 0.1667 + 0.0167 = 0.2 m²·K/W
Answer: The total thermal resistance is 0.2 m²·K/W
Most Common FAQs
Thermal resistance is a measure of how well a material or combination of materials resists the flow of heat. Higher values mean better insulation and slower heat transfer.
You need to calculate it when dealing with walls, ceilings, electronic devices, or any structure made of different materials. It helps determine how much heat will pass through and whether more insulation is need.
Yes, in building construction, R-value is a term commonly use to refer to thermal resistance. It shows how well a material insulates and is usually given per unit area.