A Divergence Angle Calculator helps measure the spread of a beam of light, laser, or any other radiative energy as it moves away from its source. This calculation is crucial in optics, laser engineering, astronomy, and other scientific applications where beam divergence affects performance and precision.
Divergence angle plays an essential role in determining beam quality, focusing ability, and efficiency in various industries, including telecommunications, medical imaging, and manufacturing. A correct calculation ensures accurate beam alignment and helps in optimizing optical systems for improved results.
Formula for Divergence Angle Calculator
The divergence angle can be calculated using the following formula:
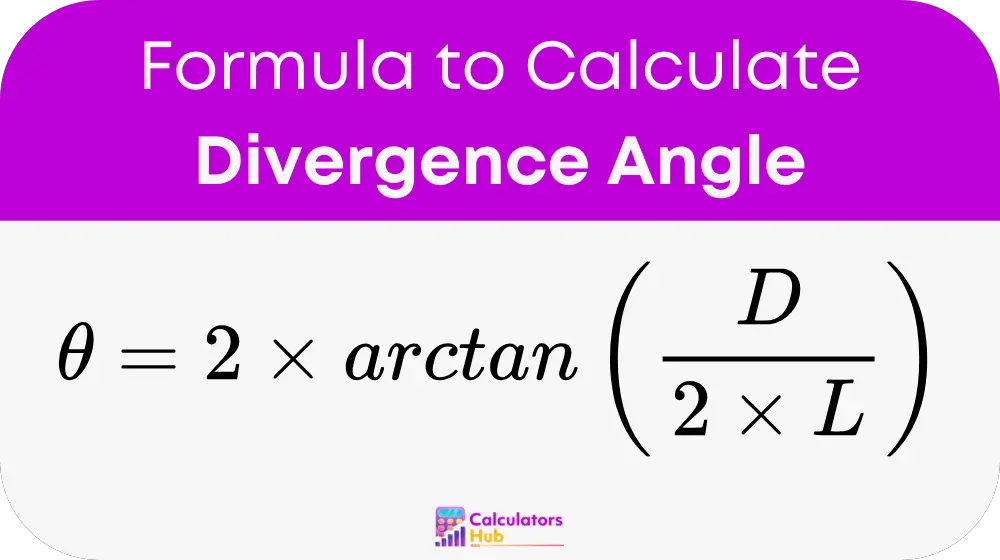
Where:
- θ (Theta): Divergence angle (in radians or degrees).
- D: Beam diameter at a given distance (meters or feet).
- L: Distance from the source to the measurement point (meters or feet).
This formula provides an accurate way to determine the beam divergence based on measurable parameters. Knowing the divergence angle is key for applications requiring high precision, such as laser cutting, satellite communications, and fiber optics.
Commonly Used Terms and Predefined Calculations
Below is a reference table with commonly used terms and estimated divergence angles for different beam types:
| Beam Type | Approximate Divergence Angle (Degrees) |
|---|---|
| Laser Pointer | 0.1 - 2 |
| LED Light | 5 - 60 |
| Flashlight Beam | 10 - 45 |
| Optical Fiber | 2 - 30 |
| Telescope Laser | 0.5 - 3 |
| Projector Beam | 10 - 25 |
The actual divergence angle can vary depending on the optics used and the beam characteristics. These values serve as general reference points for estimation.
Example of Divergence Angle Calculator
Suppose you have a laser beam with a diameter of 5 mm at a distance of 2 meters from the source. Using the formula:
Divergence Angle (\u03B8) = 2 \u00d7 arctan(5 / (2 \u00d7 2000))Converting the values into meters:
Divergence Angle (\u03B8) = 2 \u00d7 arctan(0.005 / 4)Using a scientific calculator:
\u03B8 \u2248 2 \u00d7 arctan(0.00125) \u2248 0.143 degreesThis means the laser beam has a divergence angle of approximately 0.143 degrees, which is consider very narrow, making it suitable for high-precision applications like optical communication and laser targeting.
Most Common FAQs
Calculating the divergence angle is crucial for ensuring the accuracy and efficiency of optical and laser systems. It helps optimize focusing, beam alignment, and energy distribution.
Reducing the divergence angle can be achieve by using high-quality collimating optics, such as lenses or mirrors, and by improving beam quality through better optical components and alignment techniques.
For laser communication systems, a low divergence angle (below 1 degree) is generally prefer to ensure minimal signal loss and high transmission accuracy over long distances.