The Depth of Flow in Pipe Calculator helps engineers, hydrologists, and plumbing professionals determine the depth of fluid flow inside a pipe based on various hydraulic parameters. This calculation is crucial for designing drainage systems, sewage pipelines, and water supply networks. By inputting flow rate, pipe diameter, slope, and Manning’s roughness coefficient, users can accurately estimate flow depth and optimize pipeline efficiency.
Formula of Depth Of Flow In Pipe Calculator
The depth of flow in a pipe is estimated using the Manning’s equation, which considers hydraulic factors affecting fluid motion:
Depth of Flow = Pipe Diameter × Function of (Flow Rate, Slope, Manning’s Roughness)
The general form of the Manning’s equation for open-channel and partially full pipe flow is:
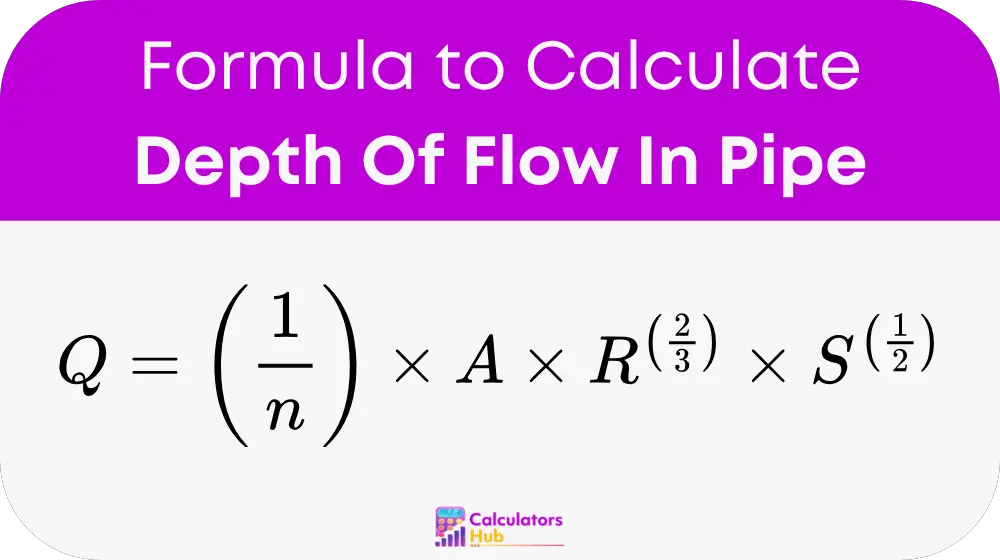
where:
- Q is the flow rate (cubic meters per second or cubic feet per second).
- n is Manning’s roughness coefficient, which depends on pipe material.
- A is the cross-sectional area of flow (square meters or square feet).
- R is the hydraulic radius (meters or feet), calculated as A/P, where P is the wetted perimeter.
- S is the slope of the pipe (meters per meter or feet per feet).
This equation helps engineers determine how full a pipe will be at a given flow rate, ensuring proper system design.
Depth of Flow Reference Table
This table provides estimated flow depths for different pipe sizes and flow conditions based on typical Manning’s roughness coefficients.
| Pipe Diameter (mm) | Flow Rate (L/s) | Slope (%) | Manning’s n | Estimated Flow Depth (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 10 | 0.5 | 0.013 | 45 |
| 300 | 50 | 1.0 | 0.012 | 120 |
| 600 | 200 | 0.75 | 0.015 | 280 |
| 900 | 500 | 1.5 | 0.014 | 450 |
| 1200 | 1000 | 1.0 | 0.013 | 700 |
These values provide a general reference for hydraulic engineers designing pipe systems.
Example of Depth Of Flow In Pipe Calculator
A civil engineer is designing a sewage pipeline using a 600 mm diameter pipe, with a flow rate of 200 L/s, a slope of 0.75%, and a Manning’s roughness coefficient of 0.015.
Using the Manning’s equation:
Q = (1/n) × A × R^(2/3) × S^(1/2)
By solving for the flow depth, the estimated value is 280 mm.
This calculation ensures the pipe is not overfilled and operates efficiently.
Most Common FAQs
The depth of flow determines whether a pipeline can handle expected discharge without overflow or excessive pressure buildup, preventing system failure.
Manning’s coefficient varies based on pipe material (e.g., concrete, PVC, steel) and surface conditions, affecting fluid resistance and flow velocity.
Yes, the Depth of Flow in Pipe Calculator is widely used in stormwater drainage design, ensuring efficient runoff management and preventing flooding.