The Compressor Exit Temperature Versus Pressure Ratio Calculator determines the final temperature of a gas after compression, based on its inlet temperature and pressure ratio. It uses thermodynamic principles to calculate temperature variations due to changes in pressure, helping engineers and system designers optimize compressor performance. This calculator is essential for preventing overheating, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring the reliability of compressors in various industries, such as HVAC, gas processing, and manufacturing.
Formula
The calculation for the exit temperature uses the following formula:
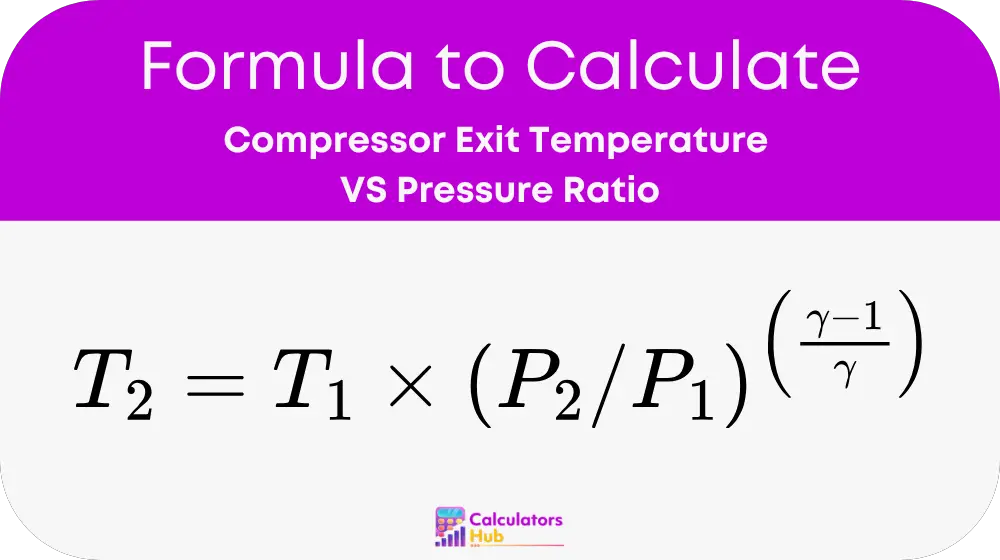
Where:
T₂ = exit (final) temperature (Kelvin).
T₁ = inlet (initial) temperature (Kelvin).
P₂ = exit (discharge) pressure (absolute).
P₁ = inlet (initial) pressure (absolute).
γ = adiabatic index (ratio of specific heats, Cₚ/Cᵥ, approximately 1.4 for air).
Relationship with Pressure Ratio
The pressure ratio (PR) is defined as: PR = P₂ / P₁. By substituting PR into the formula: T₂ = T₁ × (PR)^((γ - 1) / γ).
Steps to Calculate
- Determine the Inlet Temperature (T₁): Convert the inlet temperature to Kelvin using: T₁ (K) = T₁ (°C) + 273.15.
- Calculate or Determine the Pressure Ratio (PR): PR = P₂ / P₁.
- Use the Adiabatic Index (γ): For air, γ ≈ 1.4. For other gases, use their specific heat ratio.
- Substitute Values into the Formula: Compute the final temperature (T₂) in Kelvin using the formula: T₂ = T₁ × (PR)^((γ - 1) / γ).
- Optional Conversion to Celsius: Convert T₂ from Kelvin to Celsius using: T₂ (°C) = T₂ (K) - 273.15.
Table for Common Scenarios
Below is a pre-calculated table for typical pressure ratios, assuming T₁ = 300 K (27°C):
| Pressure Ratio (PR) | Exit Temperature (T₂, K) | Exit Temperature (T₂, °C) |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 366.1 | 93.0 |
| 3 | 419.6 | 146.5 |
| 4 | 463.4 | 190.3 |
| 5 | 500.6 | 227.4 |
This table provides a quick reference for engineers and technicians working with air compressors under standard conditions.
Example
Scenario
Air is compressed from an initial temperature of 25°C at an inlet pressure of 1 bar to a discharge pressure of 4 bar. Calculate the exit temperature of the air.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Convert Inlet Temperature (T₁) to Kelvin:
T₁ = 25 + 273.15 = 298.15 K. - Calculate the Pressure Ratio (PR):
PR = P₂ / P₁ = 4 / 1 = 4. - Apply the Formula:
T₂ = T₁ × (PR)^((γ - 1) / γ)
T₂ = 298.15 × (4)^((1.4 - 1) / 1.4)
T₂ = 298.15 × (4)^0.2857
T₂ ≈ 298.15 × 1.414
T₂ ≈ 421.85 K. - Convert to Celsius:
T₂ (°C) = T₂ (K) - 273.15
T₂ (°C) ≈ 421.85 - 273.15 ≈ 148.7°C.
Thus, the exit temperature of the air is approximately 148.7°C.
Most Common FAQs
This calculator determines the final temperature of a gas after compression, based on its initial temperature and pressure ratio. It helps in designing efficient and safe compressor systems.
Yes, it can be used for other gases. However, you need to substitute the specific adiabatic index (γ) of the gas in place of 1.4 (which is specific to air).
Temperature rises during compression because the work done on the gas increases its internal energy, in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics.