The Chilled Water Coil Performance Calculator helps engineers and HVAC professionals determine the heat transfer rate of a chilled water coil. This is essential for evaluating how effectively a coil can absorb heat from air or other substances, which is vital in air conditioning, refrigeration, and other cooling applications. By calculating the heat transfer rate, the calculator provides valuable insights into the performance of a chilled water system, helping to optimize its efficiency.
In a chilled water system, water circulates through coils and absorbs heat from the air passing over them. This cooled water is then sent back to a cooling unit, maintaining the desired temperature. The Chilled Water Coil Performance Calculator determines how much heat is being transferred from the air to the water as it moves through the coil. The formula used in this calculation involves the mass flow rate of water, the specific heat of water, and the temperature difference between the water's inlet and outlet.
Formula of Chilled Water Coil Performance Calculator
To calculate the performance of a chilled water coil, use the following formula:
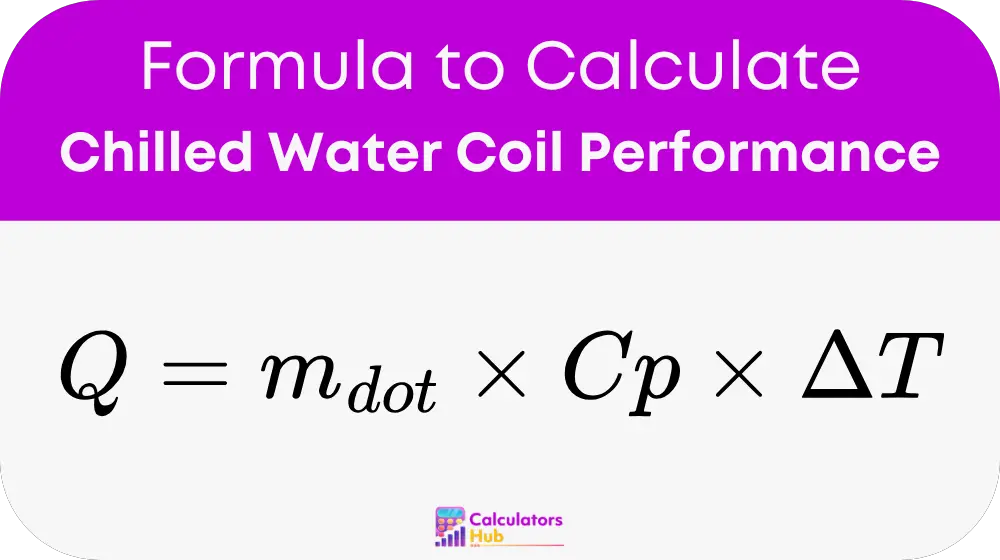
Where:
- Q: Heat transfer rate (BTU/hr) — the amount of heat being transferred through the coil per hour.
- m_dot: Mass flow rate of water (lb/hr) — the amount of water flowing through the coil in pounds per hour.
- Cp: Specific heat of water (BTU/lb°F) — the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. For water, Cp is approximately 1 BTU/lb°F.
- ΔT: Temperature difference (°F) — the difference between the inlet and outlet temperatures of the water flowing through the coil.
Steps to Calculate Performance:
- Determine Water Flow Rate (m_dot):
- Measure the flow rate of water in gallons per minute (GPM).
- Convert GPM to lb/hr: 1 GPM ≈ 500 lb/hr.
- Calculate Temperature Difference (ΔT):
- Measure the temperature of the water at the inlet and outlet of the coil.
- Subtract the outlet temperature from the inlet temperature: ΔT = T_inlet - T_outlet.
- Calculate Heat Transfer Rate (Q):
- Use the formula: Q = m_dot × Cp × ΔT.
- For water, the specific heat (Cp) is approximately 1 BTU/lb°F.
General Terms Table
Here’s a table with definitions of key terms that are commonly searched and will help with using the Chilled Water Coil Performance Calculator:
| Term | Description | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Rate (GPM) | The amount of water flowing through the system in gallons per minute | 1 to 5000 GPM |
| Mass Flow Rate (lb/hr) | The rate of water flow in pounds per hour | 500 to 250,000 lb/hr |
| Specific Heat (Cp) | The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by 1°F | 1 BTU/lb°F |
| Temperature Difference (ΔT) | The difference between the inlet and outlet water temperatures | 5°F to 50°F |
| Heat Transfer Rate (Q) | The amount of heat transferred from the air to the water per hour | Varies depending on system |
Example of Chilled Water Coil Performance Calculator
Let’s go through an example to see how to use the Chilled Water Coil Performance Calculator in a real-world scenario:
Given Data:
- Flow Rate (m_dot): 150 GPM
- Inlet Temperature (T_inlet): 50°F
- Outlet Temperature (T_outlet): 40°F
Step 1: Convert the Flow Rate to lb/hr:
Since 1 GPM ≈ 500 lb/hr, the flow rate is: 150 GPM × 500 lb/hr = 75,000 lb/hr
Step 2: Calculate the Temperature Difference (ΔT):
ΔT = T_inlet - T_outlet = 50°F - 40°F = 10°F
Step 3: Use the Formula to Calculate the Heat Transfer Rate (Q):
Using the formula Q = m_dot × Cp × ΔT, we substitute the values:
Q = 75,000 lb/hr × 1 BTU/lb°F × 10°F
Q = 750,000 BTU/hr
Result:
The heat transfer rate for this chilled water coil is 750,000 BTU/hr. This means that the coil is transferring 750,000 BTUs of heat per hour from the air to the water.
Most Common FAQs
To calculate the heat transfer rate, you need to know the mass flow rate of the water, the specific heat of water, and the temperature difference between the inlet and outlet. Use the formula Q = m_dot × Cp × ΔT where:
m_dot is the mass flow rate in lb/hr.
Cp is the specific heat of water (approximately 1 BTU/lb°F).
ΔT is the temperature difference in °F.
In most chilled water systems, the temperature difference (ΔT) typically ranges from 5°F to 15°F, depending on the system's cooling capacity and load. However, it can be higher in specific industrial applications.
To convert flow rate from gallons per minute (GPM) to pounds per hour (lb/hr), multiply the GPM by 500. This is a general conversion factor for water at standard conditions.