The CFM to Voltage Calculator is a tool used to determine the voltage output required to match a given airflow rate (CFM) in systems such as HVAC, ventilation, and industrial processes. Often used in the context of sensors or fans, this calculator helps users understand how airflow (measured in cubic feet per minute, or CFM) can be translated into a corresponding voltage output, based on specific sensor calibrations.
This calculator is particularly useful for engineers, technicians, and those working with airflow sensors that use a linear relationship between airflow and voltage. By inputting the airflow rate, users can easily compute the required voltage for their systems, which is essential for controlling motors, adjusting system settings, or performing system diagnostics.
Formula of Cfm To Voltage Calculator
The formula for calculating voltage (V) from the airflow rate (CFM) is as follows:
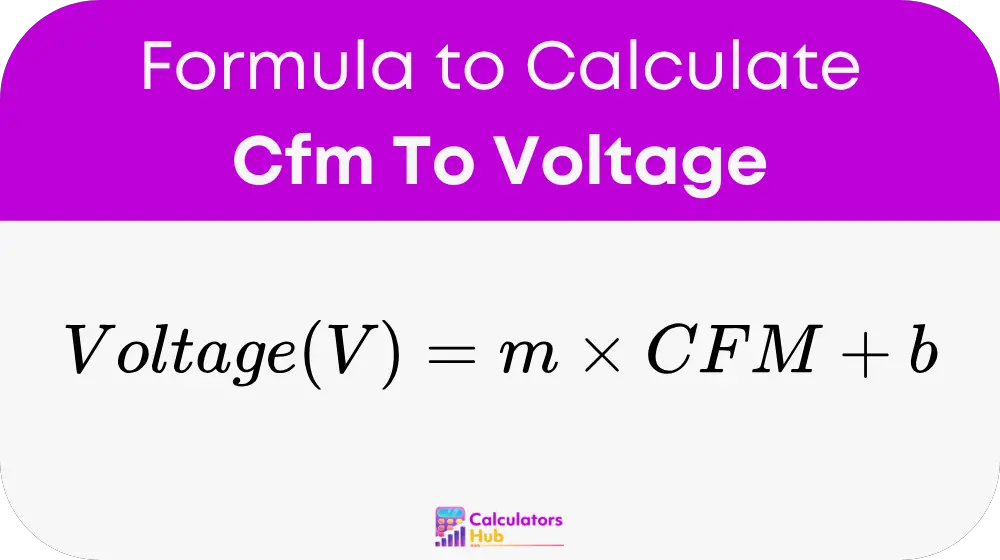
Where:
- V = Voltage output corresponding to the airflow in volts (V)
- CFM = Airflow rate in cubic feet per minute
- m = Slope of the linear relationship (volts per CFM), based on sensor calibration
- b = Offset or intercept voltage, based on sensor calibration
This equation represents a simple linear relationship where the voltage increases in proportion to the airflow, adjusted by the calibration parameters. The value of m (slope) represents how much the voltage changes per unit increase in airflow, and b (intercept) represents the baseline voltage when the airflow is zero.
General Terms for Quick Reference
For those who prefer not to perform the calculation each time, here’s a table summarizing typical values for airflow (CFM) and corresponding voltage outputs (V) based on standard sensor calibration values.
| Airflow (CFM) | Voltage Output (V) | Slope (m) | Offset (b) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | 2.5 | 0.005 | 0.5 |
| 1000 | 5.0 | 0.005 | 0.5 |
| 1500 | 7.5 | 0.005 | 0.5 |
| 2000 | 10.0 | 0.005 | 0.5 |
| 2500 | 12.5 | 0.005 | 0.5 |
This table can help users quickly determine the voltage output for common airflow rates without needing to manually perform the calculation.
Example of Cfm To Voltage Calculator
Let’s go through an example of calculating voltage based on airflow using the formula.
Given:
- Airflow (CFM) = 1200
- Slope (m) = 0.005 (volts per CFM)
- Offset (b) = 0.5 (volts)
Step 1: Plug the values into the formula:
V = m * CFM + b
V = 0.005 * 1200 + 0.5
Step 2: Perform the calculation:
V = 6 + 0.5
V = 6.5 volts
Thus, the voltage required for an airflow of 1200 CFM would be 6.5 volts.
Most Common FAQs
The CFM to Voltage calculator works by applying a linear formula that relates the airflow rate (CFM) to the voltage output. It uses calibration values, specifically the slope (m) and offset (b). To provide an accurate voltage output for a given airflow rate.
In the formula V = m * CFM + b, m is the slope of the linear relationship between airflow and voltage. Typically provided by the sensor manufacturer. b is the offset or baseline voltage when there is no airflow. These values are crucial for accurate voltage calculation based on the specific characteristics of the airflow sensor or system being used.
Yes, the CFM to Voltage calculator can be used for any system or sensor where the relationship between airflow and voltage is linear. However, it’s important to use the correct calibration values (slope m and offset b) for the specific sensor in use. As different sensors may have different characteristics.