The CFM to Static Pressure calculator is a tool used to estimate the static pressure (SP) in an HVAC system or ventilation ductwork based on the airflow rate (CFM). Static pressure is an important parameter in air-moving systems as it helps determine how much resistance the air will encounter as it moves through ducts, filters, and other components. This calculator is commonly used by engineers, HVAC professionals, and building designers to ensure that their systems are properly balanced and can effectively deliver the required airflow.
In practical terms, static pressure is a key factor in selecting the right fan or blower for a system. It also helps determine whether adjustments are needed in the ductwork to maintain efficient airflow. By calculating static pressure, users can assess the performance of their HVAC systems, troubleshoot issues, and optimize energy efficiency.
Formula of CFM to Static Pressure Calculator
The formula for calculating static pressure (SP) from the airflow rate (CFM) and the cross-sectional area of the duct is as follows:
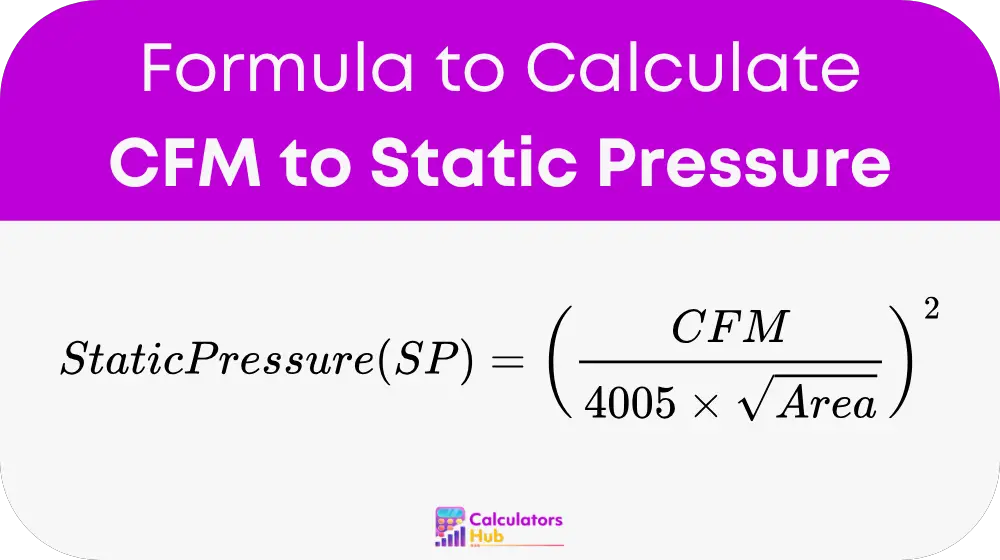
Where:
- SP = Static Pressure, in inches of water column (in. w.c.)
- CFM = Airflow in cubic feet per minute
- Area = Cross-sectional area of the duct in square feet, calculated by dividing the cross-sectional area in square inches by 144
Understanding the Formula
This formula calculates the static pressure by considering the airflow rate and the size of the duct. The cross-sectional area affects how much space the air has to move through, and as the area increases, the static pressure decreases for the same airflow rate. The constant 4005 in the formula is a conversion factor that ensures the units are compatible for static pressure calculation in inches of water column.
General Terms for Quick Reference
For those who want to avoid recalculating each time, here's a table of typical values for airflow and static pressure. This reference will help users quickly estimate the static pressure for common duct sizes and airflow rates.
| Airflow (CFM) | Duct Area (ft²) | Static Pressure (in. w.c.) |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | 0.5 | 0.20 |
| 1000 | 1.0 | 0.09 |
| 1500 | 1.5 | 0.06 |
| 2000 | 2.0 | 0.05 |
| 2500 | 2.5 | 0.04 |
This table provides a quick reference to calculate static pressure based on common airflow values and duct areas. It can help professionals avoid repeated calculations, especially when dealing with similar ductwork sizes.
Example of CFM to Static Pressure Calculator
Let’s go through an example of calculating static pressure for a ventilation system.
Assume that the airflow (CFM) is 1500 and the duct has a cross-sectional area of 2 square feet.
- Plug the values into the formula:SP = ((1500 / (4005 * √(2)))^2)
- Simplify the calculation:First, calculate the square root of 2: √2 ≈ 1.414Then, calculate the denominator: 4005 * 1.414 ≈ 5668.07Now, calculate the division: 1500 / 5668.07 ≈ 0.264Finally, square the result: 0.264^2 ≈ 0.070
Thus, the static pressure (SP) is approximately 0.070 inches of water column.
Most Common FAQs
To calculate static pressure, use the formula: SP = ((CFM / (4005 * √(Area)))^2).
Make sure to know the airflow rate (CFM) and the cross-sectional area of the duct in square feet to use in the calculation.
Static pressure is crucial because it indicates the resistance the air encounters as it moves through the system. If the static pressure is too high, it can lead to reduced airflow and energy inefficiency. Conversely, low static pressure may indicate insufficient resistance or a poorly sized duct system.
Yes, this calculator can be used for both round and rectangular ducts, as long as the cross-sectional area is properly calculated. For round ducts, use the formula for the area of a circle (A = π * (D/2)²). For rectangular ducts, simply multiply the width and height of the duct to get the area (A = W * H).