The Annual Heat Loss Calculator is an essential tool used by architects, builders, and homeowners to estimate the energy efficiency of buildings. This calculator helps in determining the amount of heat that escapes from a building throughout a year, providing crucial data for improving insulation and reducing energy costs. Understanding and managing heat loss is fundamental for constructing energy-efficient homes and buildings, aligning with sustainability goals.
Formula of Annual Heat Loss Calculator
The formula to calculate Annual Heat Loss (Q) in a building is as follows:
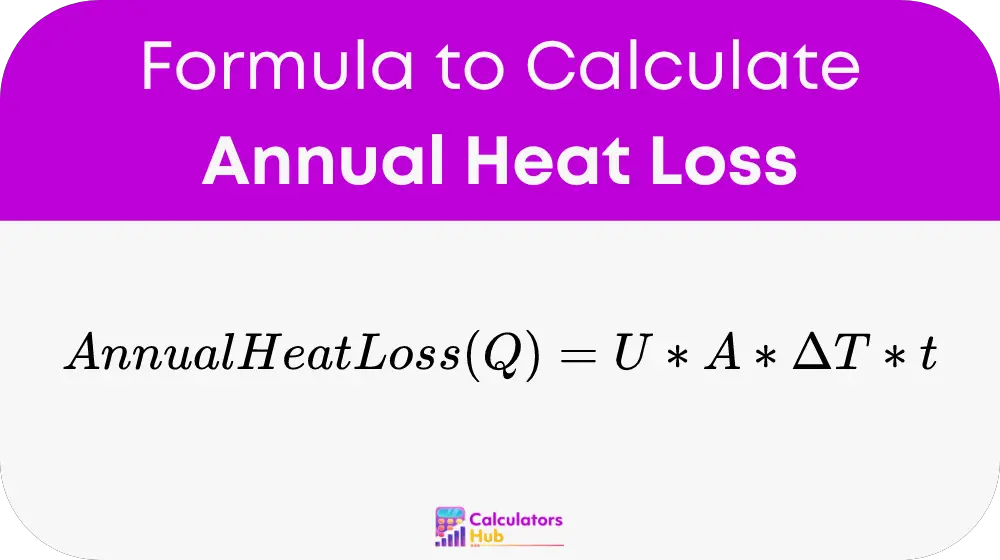
Where:
- U (Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient): Measured in watts per square meter per degree Celsius (W/m²·°C), indicating the thermal conductivity of the building materials.
- A (Surface Area): The total area in square meters (m²) through which heat is lost.
- ΔT (Temperature Difference): The degree Celsius (°C) difference between the interior and exterior of the building.
- t (Time Period): Typically one year, expressed in hours (commonly 8760 hours).
Table of General Terms
To assist users in navigating through calculations, here’s a table explaining key terms associated with heat loss:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| U-Value | A measure of the thermal conductivity of building materials, influencing how quickly heat is lost. |
| Surface Area (A) | Area through which heat is transferred, affecting the total heat loss. |
| Temperature Difference (ΔT) | The difference in temperature inside versus outside, driving the need for heating or cooling. |
| Annual Heat Loss (Q) | The total heat lost from a building over the course of a year, important for energy management and insulation planning. |
Example of Annual Heat Loss Calculator
Consider a building with a surface area of 300 m², a U-value of 0.35 W/m²·°C, and an average temperature difference (ΔT) of 20°C throughout the year. Using our formula, the annual heat loss would be calculate as:
Annual Heat Loss (Q) = 0.35 * 300 * 20 * 8760 = 1,836,800 Wh/year
This example highlights the significant impact of insulation quality and temperature differences on a building's energy efficiency.
Most Common FAQs
Improving insulation, upgrading windows, and sealing leaks are effective ways to reduce heat loss and enhance energy efficiency.
The U-value is crucial as it quantifies the rate of heat transfer through building materials. Lower U-values indicate better insulation properties.
Yes, the calculator is versatile and can be adjust for any climatic conditions by modifying the temperature difference (ΔT) parameter.