The heparin dosage calculator is a critical tool designed to aid clinicians in administering precise amounts of heparin, based on patient-specific factors and clinical goals. By ensuring the correct dosage, this tool significantly enhances patient safety and the effectiveness of treatment regimens.
Formula of Heparin Dosage Calculator
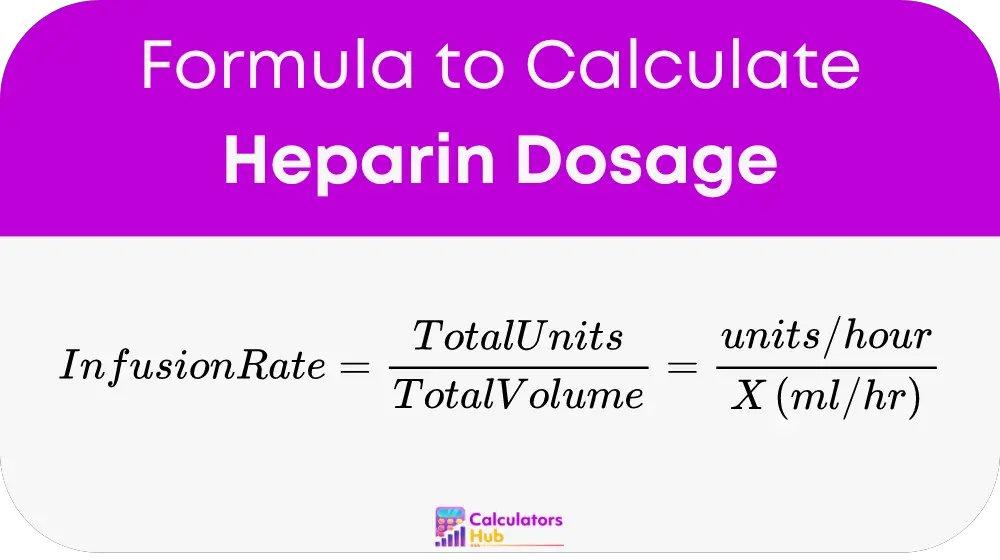
To calculate the heparin infusion rate, use the formula:
Heparin Dosage Quick Reference Table
Here’s a simple table to help healthcare providers quickly determine heparin infusion rates based on commonly encountered scenarios in clinical settings:
| Desired Heparin Dose (units/hour) | Total Heparin in Bag (units) | IV Bag Volume (ml) | Infusion Rate (ml/hour) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 25,000 | 500 | 20 |
| 1200 | 25,000 | 500 | 24 |
| 1500 | 25,000 | 500 | 30 |
| 1800 | 25,000 | 500 | 36 |
This table provides the infusion rates needed to achieve various desired doses using a standard 25,000 unit heparin bag diluted in 500 ml of IV fluid.
Example of Heparin Dosage Calculator
Scenario: A clinician needs to administer a moderate dose of heparin for a patient with a higher risk of thrombosis. The desired dose is 1500 units per hour.
Using the Table:
- Look for the desired dose in the table, which is 1500 units per hour.
- Find the corresponding infusion rate from the table, which is 30 ml per hour.
Calculation Confirmation:
Using the formula: Heparin Infusion Rate equals (Total Units in IV bag divided by Total Volume in ml) equals (Units per hour divided by X in ml per hour)
Plugging in the values: Heparin Infusion Rate: 25,000 units divided by 500 ml equals 1500 units per hour divided by X ml per hour 25,000 units times X ml per hour equals 750,000 X ml per hour equals 750,000 divided by 25,000 X equals 30 ml per hour
This calculation confirms that setting the infusion rate to 30 ml per hour will deliver 1500 units of heparin per hour, as required for this patient.
Most Common FAQs
A: The calculator is design to be highly accurate, but always verify calculations according to the latest clinical guidelines.
A: Dosages should be reviewed each time a patient’s condition changes or as per the clinical protocol, typically every 24 hours.
A: Yes, with appropriate adjustments for body weight and specific pediatric guidelines.