The Fio2/Pao2 Ratio Calculator, often called the P/F Ratio Calculator, is a vital tool in respiratory medicine and critical care. It quickly estimates how well oxygen is transferring from the lungs into the blood. This ratio helps doctors evaluate the severity of hypoxemia (low blood oxygen) and diagnose conditions like Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). The calculator simplifies what would otherwise require more complex lung function tests, offering clinicians an evidence-based way to guide oxygen therapy and ventilation decisions at the bedside.
This calculator is categorized under Clinical Respiratory Calculators and Critical Care Assessment Tools.
Formula of Fio2/Pao2 Ratio Calculator
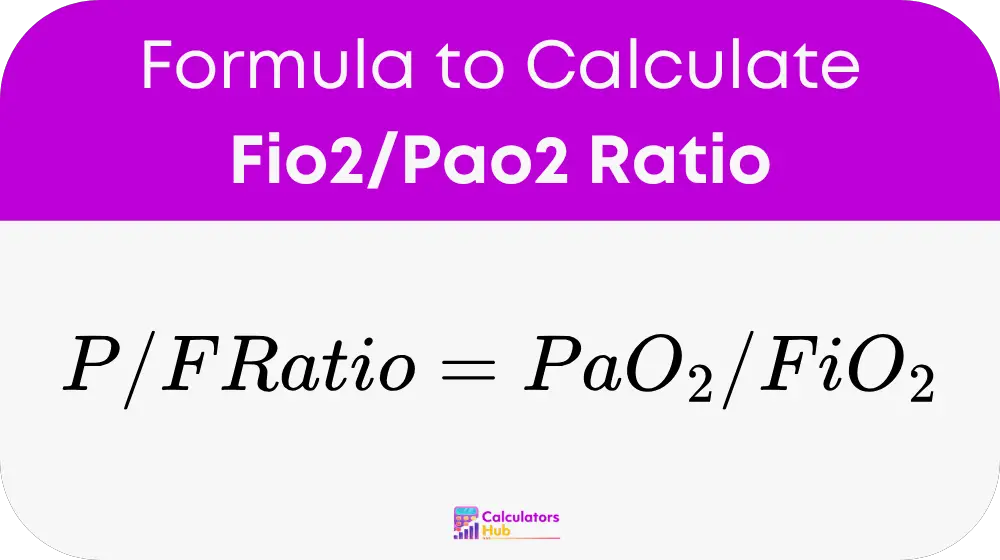
Where:
- PaO₂ = Arterial partial pressure of oxygen (measured in mmHg)
- FiO₂ = Fraction of inspired oxygen (entered as a decimal)
Important Note:
If FiO₂ is given as a percentage, convert it to a decimal before using the formula:
FiO₂ (decimal) = FiO₂ (%) / 100
P/F Ratio Severity Reference Table
| P/F Ratio Range | Clinical Interpretation | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| > 300 | Normal or mild oxygenation issue | Mild |
| 200–300 | Mild ARDS | Mild |
| 100–200 | Moderate ARDS | Moderate |
| < 100 | Severe ARDS | Severe |
This table helps clinicians understand the patient’s respiratory condition quickly.
Example of Fio2/Pao2 Ratio Calculator
A patient has a PaO₂ of 70 mmHg while breathing 50% oxygen.
Step 1: Convert FiO₂ to decimal: 50% → 0.50
Step 2: Apply formula: P/F Ratio = 70 / 0.50 = 140
Interpretation:
A P/F ratio of 140 indicates moderate hypoxemia and may meet criteria for moderate ARDS. Clinicians may adjust ventilator settings or escalate care based on this value.
Most Common FAQs
A normal P/F Ratio in a healthy adult is typically greater than 300 mmHg. Values below 300 suggest impaired oxygen exchange.
It helps assess lung function in critically ill patients and is part of ARDS diagnostic criteria. It informs how aggressively oxygen therapy or ventilation support should be adjusted.
No. This ratio requires an arterial blood gas test (PaO₂) and precise FiO₂, usually obtained in a hospital or clinical setting.