CPO is a critical metric in cardiovascular health, representing the overall power the heart generates during each minute of activity. The Cardiac Power Output Calculator aids in computing this value efficiently, ensuring healthcare providers can quickly evaluate a patient’s cardiac health and make informed clinical decisions.
Formula of Cardiac Power Output Calculator
The formula to calculate CPO is straightforward yet powerful:
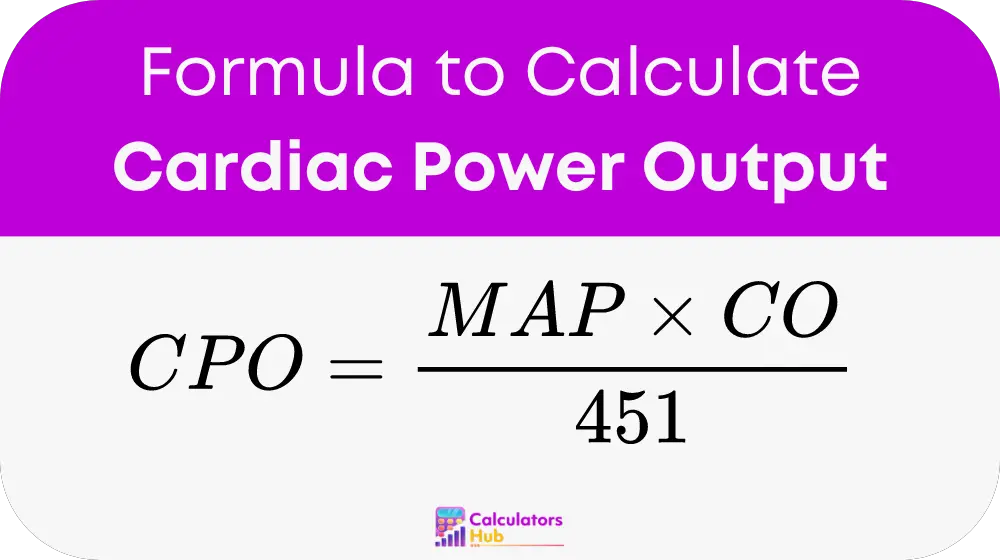
- Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP): MAP is the average pressure in a patient’s arteries during one cardiac cycle and is typically measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). It is crucial for understanding blood flow resistance and overall arterial health.
- Cardiac Output (CO): CO measures the volume of blood the heart pumps in a minute, expressed in liters per minute (L/min). It is a fundamental indicator of cardiac function and overall blood circulation efficiency.
Useful Conversion Table
To aid in the practical application of the CPO calculation, here is a conversion table that includes essential metrics relevant to the formula:
| Term | Definition | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|
| MAP | Mean arterial pressure in mmHg | N/A |
| CO | Cardiac output in L/min | N/A |
| (Note: Further details can be filled in based on user-specific needs and common queries.) |
Example of Cardiac Power Output Calculator
Let’s consider a practical example to illustrate the use of the CPO calculator:
- Scenario: A patient with a MAP of 93 mmHg and a CO of 5.2 L/min.
- Calculation: CPO = (93 × 5.2) / 451 = 1.07 W This example shows how the calculator can be used in clinical settings to assess cardiac efficiency.
Most Common FAQs
The normal range for CPO varies, but generally, a value between 0.5 and 1.0 Watts is considered normal for adults.
Significant deviations from the normal CPO range can indicate cardiac dysfunction, prompting further diagnostic testing or treatment adjustments.
While the CPO calculator is a valuable tool, it should be use as part of a comprehensive assessment, considering other clinical factors and individual patient circumstances.