The Bateman Equation Calculator helps predict the concentration of a drug in plasma at different times after administration. Users enter specific values related to the drug's properties and the patient’s characteristics, and the calculator uses these inputs to compute drug levels. This is critical for designing effective dosing schedules and understanding drug interactions within the human body.
Formula of Bateman Equation Calculator
The Bateman equation for drug concentration in plasma after oral administration is given by:
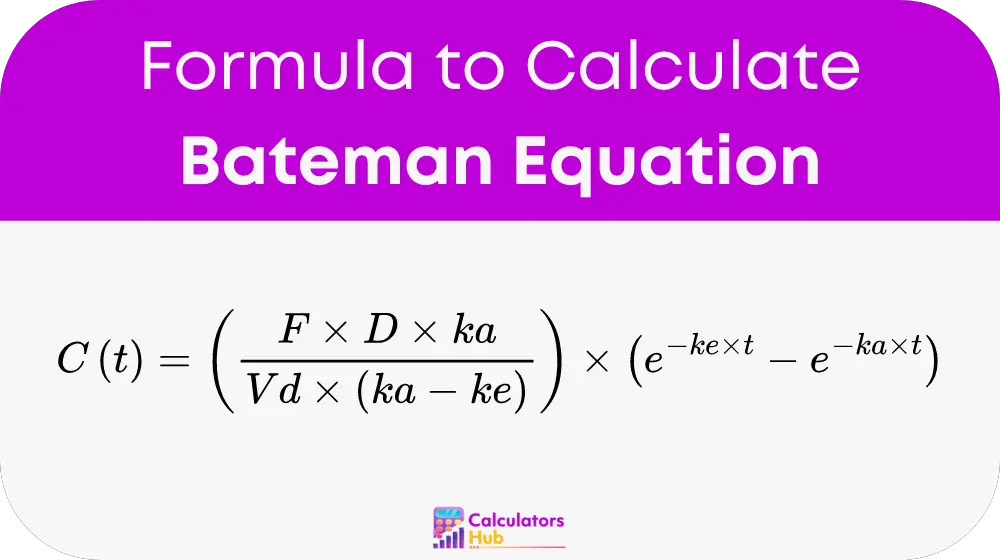
Where:
- C(t) is the concentration of the drug in the plasma at time t.
- F represents the bioavailability of the drug, the fraction of the administered dose that reaches systemic circulation.
- D is the dose of the drug administered.
- ka is the absorption rate constant.
- ke is the elimination rate constant.
- Vd is the volume of distribution.
- t is the time after drug administration.
Steps to Use the Bateman Equation in a Calculator:
- Identify the Variables:
- Bioavailability (F)
- Dose (D)
- Absorption rate constant (ka)
- Elimination rate constant (ke)
- Volume of distribution (Vd)
- Time (t)
- Apply the Bateman Equation:
- Use the identified values and plug them into the equation.
- Perform the Calculation:
- First, calculate the constants in the equation: F * D * ka / (Vd * (ka - ke))
- Then, compute the two exponential terms: e^(-ke * t) and e^(-ka * t)
- Subtract the second exponential term from the first and multiply by the constants to get C(t).
Table of Typical Values
Here is a table of typical values for the Bateman Equation parameters to aid in using the calculator effectively:
| Parameter | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| Bioavailability (F) | 0.5 - 1.0 |
| Dose (D) | 100 - 500 mg |
| Absorption rate constant (ka) | 1.0 - 1.5 hr^-1 |
| Elimination rate constant (ke) | 0.1 - 0.7 hr^-1 |
| Volume of distribution (Vd) | 10 - 100 L |
| Time (t) | 1 - 24 hours |
Example of Bateman Equation Calculator
Let’s calculate the plasma concentration of a drug 3 hours after oral administration with the following values: F = 0.8, D = 200 mg, ka = 1.2 hr^-1, ke = 0.5 hr^-1, Vd = 50 L.
- Calculate the constants: 0.8 * 200 * 1.2 / (50 * (1.2 - 0.5)) = 3.6571
- Compute the exponential terms: e^(-0.5 * 3) = 0.2231, e^(-1.2 * 3) = 0.0498
- Perform the final calculation: 3.6571 * (0.2231 - 0.0498) = 0.6332 mg/L
Most Common FAQs
Bioavailability is the fraction of an administered dose of unchanged drug that reaches the systemic circulation, crucial for understanding how much of the drug administered can actually affect the body.
The time variable in the Bateman Equation allows us to predict how the concentration of a drug changes as it gets absorbed and eliminated over time. This helps in planning the frequency and dosage of medication.