The Deposit Growth Calculator helps individuals and businesses estimate the future value of a savings deposit based on interest rate, compounding frequency, and investment duration. This tool is essential for financial planning, allowing users to forecast how their money will grow over time in bank accounts, fixed deposits, or investment savings. By using this calculator, savers can make informed decisions about where to invest their funds and maximize returns.
Formula of Deposit Growth Calculator
Deposit Growth is calculated using the compound interest formula:
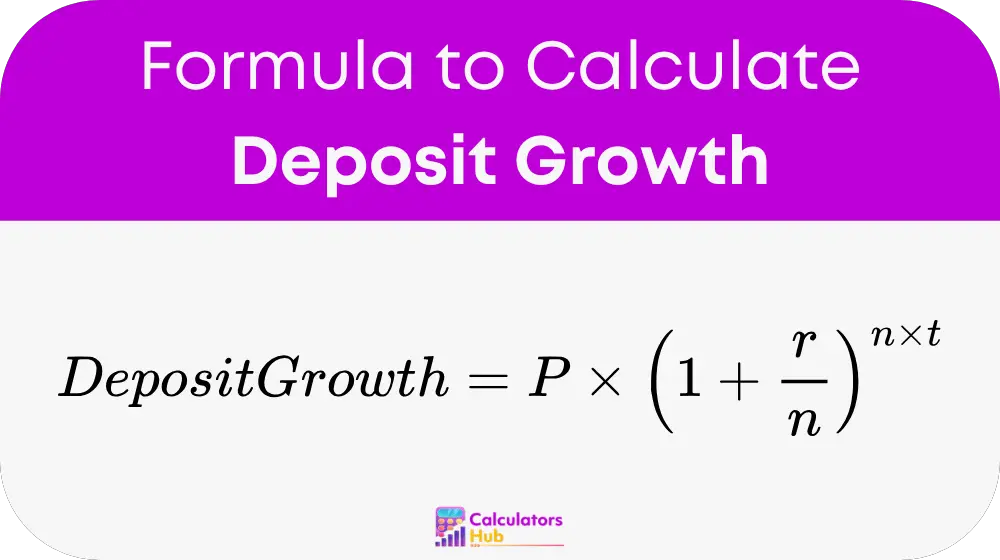
where:
- P is the initial deposit (principal amount).
- r is the annual interest rate (expressed as a decimal, e.g., 5% = 0.05).
- n is the number of times interest is compounded per year (e.g., 12 for monthly, 4 for quarterly).
- t is the total number of years.
This formula accounts for the effects of compounding, ensuring an accurate estimate of deposit growth over time.
Deposit Growth Reference Table
This table provides estimated deposit growth values for different initial deposits and interest rates over a 10-year period with monthly compounding.
| Initial Deposit ($) | Annual Interest Rate (%) | Years | Compounded Monthly | Final Amount ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000 | 3.0 | 10 | Yes | 1,349 |
| 5,000 | 4.5 | 10 | Yes | 7,819 |
| 10,000 | 5.0 | 10 | Yes | 16,470 |
| 20,000 | 6.0 | 10 | Yes | 35,898 |
| 50,000 | 7.0 | 10 | Yes | 102,511 |
These values illustrate how different principal amounts and interest rates affect deposit growth.
Example of Deposit Growth Calculator
A person deposits $10,000 in a savings account that offers an annual interest rate of 5%, compounded monthly, for 5 years. Using the formula:
Deposit Growth = 10,000 × (1 + 0.05/12)^(12 × 5)
= 10,000 × (1.004167)^(60)
= 10,000 × 1.28336
≈ $12,833.60
This means that after 5 years, the initial deposit will grow to approximately $12,833.60.
Most Common FAQs
Compound interest allows savings to grow faster by earning interest on both the initial deposit and previously earned interest, making it a powerful tool for long-term financial planning.
The more frequently interest is compounded (daily, monthly, quarterly), the higher the total deposit growth. Monthly and daily compounding generate more interest compared to annual compounding.