The Benefit to Cost Ratio (BCR) Calculator is a vital tool used in financial analysis, project management, and economic evaluation to determine the feasibility and profitability of a project or investment. This ratio compares the total expected benefits of a project to its total costs, providing a clear indication of whether the project is likely to generate more value than it consumes. By using the BCR Calculator, businesses, investors, and decision-makers can assess the potential return on investment (ROI) and make informed decisions about whether to proceed with, modify, or abandon a project.
The BCR is particularly useful in evaluating public sector projects, infrastructure investments, and long-term business strategies, where both tangible and intangible benefits need to be weighed against the associated costs.
Formula of Benefit to Cost Ratio Calculator
The formula used to calculate the Benefit-to-Cost Ratio (BCR) is:
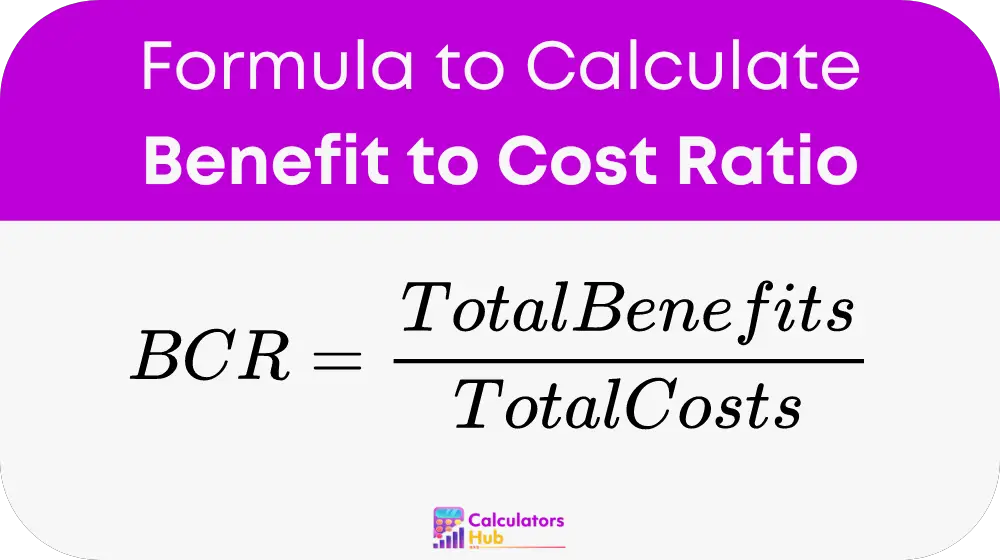
Where:
- BCR is the Benefit-to-Cost Ratio.
- Total Benefits is the sum of all benefits derived from the project, measured in monetary terms (e.g., dollars, euros).
- Total Costs is the sum of all costs associated with the project, also measured in monetary terms.
Interpretation of the BCR:
- BCR > 1: The benefits outweigh the costs, indicating a potentially profitable or worthwhile project.
- BCR = 1: The benefits are equal to the costs, suggesting a break-even situation where the project may neither gain nor lose value.
- BCR < 1: The costs outweigh the benefits, indicating that the project may not be financially viable.
This formula is straightforward yet powerful, providing a quick and effective way to assess the financial viability of a project.
Useful Conversion Table
To assist with common calculations related to the Benefit-to-Cost Ratio, the following table provides typical values and their interpretations that are frequently used in financial analysis and project management.
| Term | Description | Common Values |
|---|---|---|
| Total Benefits (USD) | The total monetary value of all benefits from the project. | $100,000, $500,000, $1,000,000 |
| Total Costs (USD) | The total monetary value of all costs associated with the project. | $50,000, $200,000, $800,000 |
| Benefit-to-Cost Ratio (BCR) | The ratio of total benefits to total costs. | 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 |
This table provides a quick reference for understanding how different benefit and cost values translate into the BCR, helping users to quickly assess the financial viability of their projects.
Example of Benefit to Cost Ratio Calculator
Let’s consider an example where you need to evaluate the financial viability of a new infrastructure project. Assume the following:
- Total Benefits: $750,000
- Total Costs: $500,000
Calculation
Using the formula:
BCR = Total Benefits / Total Costs
Substitute the values:
BCR = $750,000 / $500,000 BCR = 1.5
Interpretation
A BCR of 1.5 indicates that for every dollar spent on the project, the expected return is $1.50. This suggests that the project is financially viable and likely to generate more benefits than costs, making it a potentially profitable investment.
Most Common FAQs
The Benefit-to-Cost Ratio is important because it provides a clear and straightforward measure of a project's financial viability. By comparing the total benefits to the total costs, decision-makers can quickly determine whether a project is likely to be profitable or if it needs to be reconsidered. This ratio is especially useful in scenarios where resources are limited and must be allocated to the most beneficial projects.
To improve the Benefit-to-Cost Ratio, you can either increase the projected benefits or reduce the associated costs. Increasing benefits might involve enhancing the project's scope, finding additional revenue streams, or improving efficiency. Reducing costs might involve cutting unnecessary expenses, negotiating better terms with suppliers, or optimizing resource allocation.
Yes, the BCR can include both financial and non-financial benefits, as long as they can be quantified in monetary terms. Non-financial benefits might include social, environmental, or strategic advantages that can be assign a dollar value. Including these benefits in the BCR calculation provides a more comprehensive view of the project's overall value.