Average Per Cover:
This calculator helps restaurant managers and owners measure the average amount spent by each guest. By understanding this metric, businesses can make informed decisions about menu pricing, promotional strategies, and overall customer service enhancements. It serves as a critical indicator of both customer spending habits and the restaurant’s appeal in the market.
Formula of Average Per Cover Calculator
To calculate the average per cover, the following formula is employed:
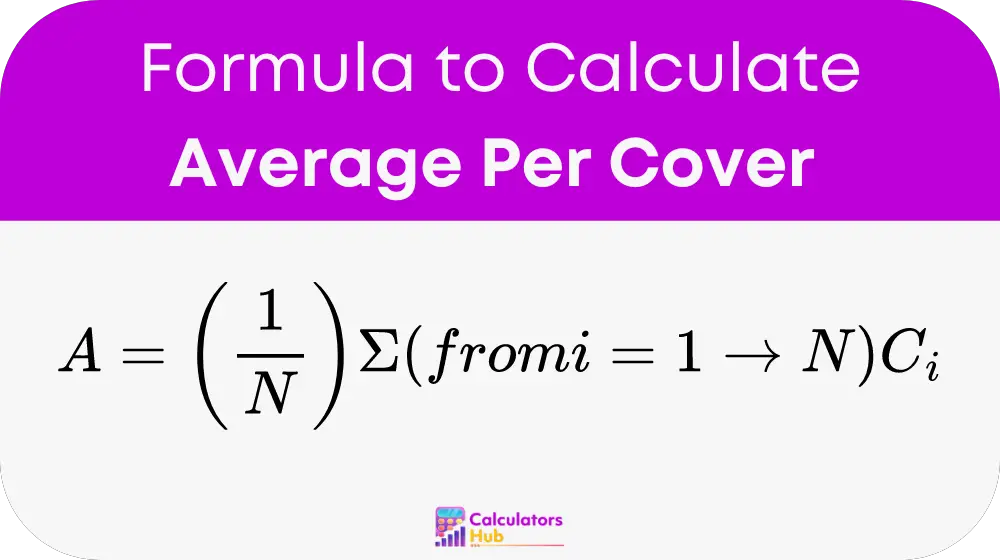
Where:
- A is the average per cover.
- N is the number of covers (guests or diners).
- C_i is the total value or cost associated with the i-th cover.
This calculation aggregates the total spent by all diners and divides it by the number of diners to determine the average expenditure per diner.
Table for General Terms
To assist users in better understanding the application of the Average Per Cover Calculator, the following table outlines common terms used in relation to this tool:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| A | Average per cover, representing average revenue per guest |
| N | Number of covers or guests |
| C_i | Total revenue associated with the i-th guest or diner |
Example of Average Per Cover Calculator
Imagine a restaurant that wants to calculate its average per cover for a particular night. Suppose there were 100 diners, and the total revenue generated was $3000. Using the formula:
A = (1/100) × 3000 = $30
This result indicates that, on average, each diner spent $30.
Most Common FAQs
A1: This metric is crucial as it helps restaurant owners and managers gauge the effectiveness of their menu pricing and understand customer spending habits. It aids in making strategic decisions regarding menu adjustments and pricing to optimize revenue.
A2: Improving the average per cover can lead to increased profitability. Strategies such as enhancing menu offerings, improving service quality, and creating a more appealing dining atmosphere can encourage guests to spend more.
A3: Yes, the average per cover can vary depending on the day of the week, time of day, and season. Understanding these patterns can help restaurants tailor their staffing, inventory, and promotional activities to meet demand and maximize revenue.