The APYE Calculator is a crucial tool designed to provide individuals with a clearer understanding of the enhanced annual percentage yield on their investments or savings. This measure is vital for anyone looking to optimize their financial returns by accurately evaluating their earnings over a specified period.
Formula of APYE Calculator
The formula to calculate APYE is:
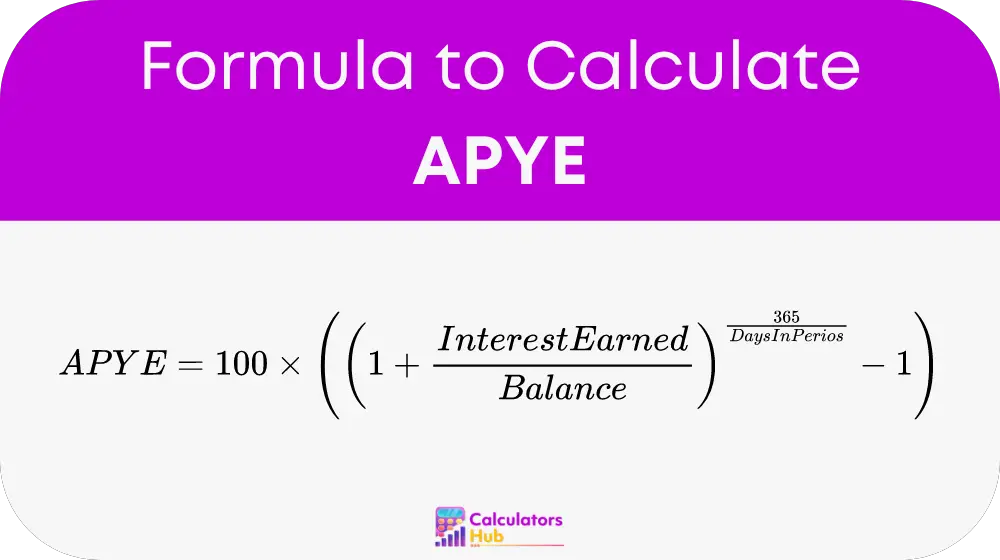
This formula calculates the effective annual interest rate considering compounding over the year.
Understanding the Variables
Interest Earned: This is the actual amount of interest you have accrued during the statement period, which can be find on your bank statement.
Balance: The average daily balance is a crucial figure, representing the average amount held in the account throughout the statement period. Different methods might be used to calculate this, so it's best to check with your bank for specifics.
Days in Period: This refers to the number of days in the statement period for which the APYE is being calculated.
Useful Conversion Table
Here is a table with common terms related to APYE calculations:
| Term | Description | Typical Values |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Earned | Amount of interest earned | Based on statements |
| Balance | Average daily balance during period | Based on calculations |
| Days in Period | Number of days in the statement period | Usually 30 or 31 |
Example of APYE Calculator
Consider a scenario where you earn $50 in interest on an average balance of $1000 over a period of 30 days. Using the formula:
APYE = 100 * ((1 + (50 / 1000)) ^ (365 / 30) - 1)
Calculating this gives us the APYE, showing the effective annual rate based on the conditions given.
Most Common FAQs
APY refers to Annual Percentage Yield, considering yearly compounding. While APYE gives a more detail view base on specific earning periods.
Higher frequency of compounding generally results in a higher APYE, showing increased earnings.
APYE calculations are useful for comparing savings accounts, investment products, or understanding financial products where interest compounds over different periods.