The Aerodynamic Diameter Calculator is an essential tool in fields such as environmental science, aerosol physics, and air quality control. It calculates the aerodynamic diameter of particles, which is crucial for understanding how particles behave in the atmosphere, including their transport, deposition, and removal processes. This diameter helps professionals predict how particles will interact with human respiratory systems and is key in designing effective air filtration systems.
Formula of Aerodynamic Diameter Calculator
The detailed formula for calculating the aerodynamic diameter is:
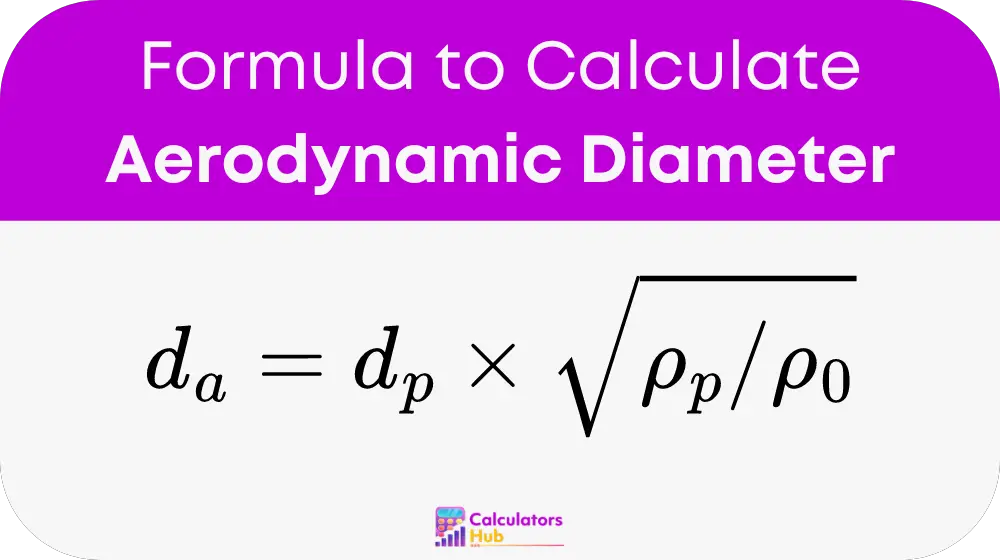
Where:
- d_a: Aerodynamic diameter
- d_p: Actual diameter of the particle
- ρ_p: Density of the particle
- ρ_0: Reference density (typically 1 g/cm³ for water)
Expanding the Formula
- Measure the actual diameter of the particle (d_p):
- This is usually measured in micrometers (µm).
- Determine the density of the particle (ρ_p):
- Density should be measured in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
- Use the reference density (ρ_0):
- Typically, ρ_0 is 1 g/cm³ if water is used as a reference.
Using these inputs, the formula simplifies to: d_a = d_p * sqrt(ρ_p / 1)
Table for General Terms and Quick Calculations
This table provides definitions and calculations for common terms related to the Aerodynamic Diameter Calculator:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Aerodynamic Diameter (d_a) | Calculated diameter reflecting particle behavior in air. |
| Actual Diameter (d_p) | Physical diameter of the particle. |
| Particle Density (ρ_p) | Density of the particle measured in g/cm³. |
| Reference Density (ρ_0) | Standard density against which measurements are made, usually 1 g/cm³. |
Quick Calculations:
| Actual Diameter (d_p) | Particle Density (ρ_p) | Aerodynamic Diameter (d_a) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 µm | 2 g/cm³ | 1.41 µm |
| 0.5 µm | 1.5 g/cm³ | 0.61 µm |
| 2 µm | 0.5 g/cm³ | 1.41 µm |
Example of Aerodynamic Diameter Calculator
Let's consider a practical example to demonstrate how to calculate the aerodynamic diameter:
- Actual Diameter (d_p): 2 µm
- Particle Density (ρ_p): 1.2 g/cm³
Calculation:
- d_a = 2 * sqrt(1.2 / 1)
- d_a = 2 * 1.095 = 2.19 µm
This example shows that the aerodynamic diameter of a particle with an actual diameter of 2 µm and a density of 1.2 g/cm³ is approximately 2.19 µm.
Most Common FAQs
A1: It is crucial for understanding how particles will settle in the environment and interact with human respiratory systems, influencing health risk assessments and air filtration designs.
A2: Yes, because aerodynamic diameter also considers the particle's density, which affects how it behaves in a fluid like air.
A3: Humidity can cause hygroscopic particles to absorb moisture, potentially increasing their actual and aerodynamic diameters.