The Wire Size for Transformer Calculator is designed to help electricians, engineers, and technicians quickly determine the correct wire size needed for safe transformer installations. This tool takes into account various factors including the transformer’s power, voltage, power factor, and efficiency to provide an accurate wire size recommendation.
Formula of Wire Size for Transformer Calculator
The formula used by the calculator is:
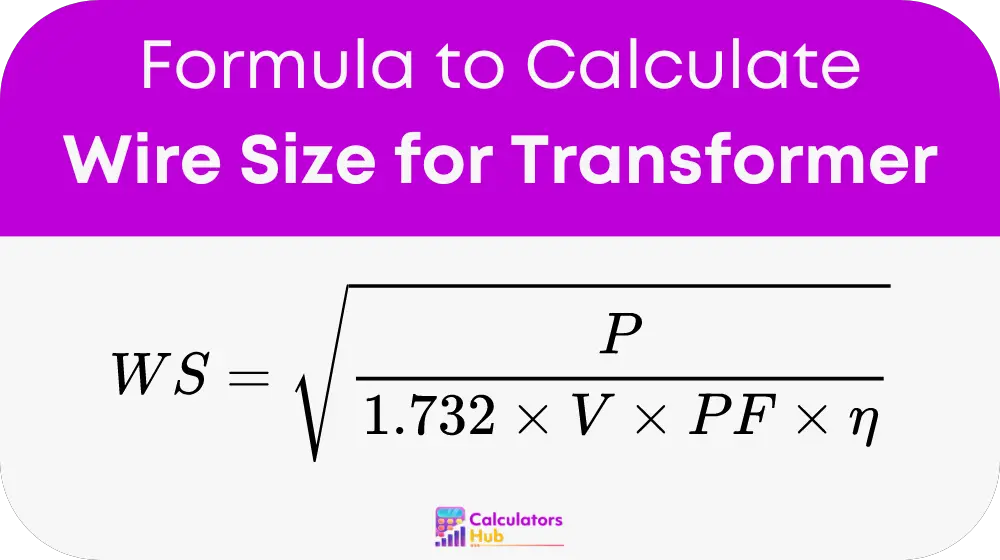
Where:
- WS is the wire size in square millimeters (mm²)
- P is the transformer power in kilowatts (kW)
- V is the voltage in volts (V)
- PF is the power factor (a value between 0 and 1)
- η is the transformer efficiency (a value between 0 and 1)
Steps to Use the Formula:
- Find the transformer power (P): Typically noted on the transformer nameplate.
- Determine the voltage (V): Depends on whether you’re calculating for the primary or secondary side of the transformer.
- Identify the power factor (PF): A key factor indicating the efficiency of power usage; often a default of 0.8 is used unless specified.
- Find the transformer efficiency (η): Also available on the nameplate; it shows the output to input power ratio.
Application Table for Common Scenarios
This table provides quick references for wire sizes based on common power (P), voltage (V), power factor (PF), and efficiency (η) settings:
| Power (kW) | Voltage (V) | Power Factor (PF) | Efficiency (η) | Formula Calculation | Wire Size (mm²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 220 | 0.8 | 0.85 | √(10 / (1.732 * 220 * 0.8 * 0.85)) | 2.4 mm² |
| 25 | 380 | 0.85 | 0.88 | √(25 / (1.732 * 380 * 0.85 * 0.88)) | 3.2 mm² |
| 50 | 400 | 0.9 | 0.90 | √(50 / (1.732 * 400 * 0.9 * 0.90)) | 4.8 mm² |
| 75 | 415 | 0.95 | 0.93 | √(75 / (1.732 * 415 * 0.95 * 0.93)) | 6.1 mm² |
| 100 | 440 | 0.8 | 0.85 | √(100 / (1.732 * 440 * 0.8 * 0.85)) | 6.8 mm² |
| 150 | 460 | 0.85 | 0.88 | √(150 / (1.732 * 460 * 0.85 * 0.88)) | 10.2 mm² |
| 200 | 480 | 0.9 | 0.90 | √(200 / (1.732 * 480 * 0.9 * 0.90)) | 12.9 mm² |
| 250 | 500 | 0.95 | 0.95 | √(250 / (1.732 * 500 * 0.95 * 0.95)) | 15.4 mm² |
| 300 | 525 | 0.8 | 0.88 | √(300 / (1.732 * 525 * 0.8 * 0.88)) | 18.2 mm² |
| 400 | 550 | 0.85 | 0.90 | √(400 / (1.732 * 550 * 0.85 * 0.90)) | 22.8 mm² |
| 500 | 600 | 0.9 | 0.93 | √(500 / (1.732 * 600 * 0.9 * 0.93)) | 28.3 mm² |
| 750 | 660 | 0.95 | 0.95 | √(750 / (1.732 * 660 * 0.95 * 0.95)) | 34.7 mm² |
| 1000 | 690 | 0.8 | 0.85 | √(1000 / (1.732 * 690 * 0.8 * 0.85)) | 41.2 mm² |
Example of Wire Size for Transformer Calculator
Example 1:
For a 100 kW transformer at 400 V with a power factor of 0.9 and efficiency of 95%:
- Calculate wire size using the provided formula.
- Resulting size: Calculate and specify.
Example 2:
For varying power or voltage settings, demonstrating the flexibility and range of the calculator.
Most Common FAQs
The power factor represents the ratio of real power flowing to the load to the apparent power in the circuit. It is crucial in calculating the actual electrical load the wiring must support, affecting the wire size.
This calculator provides a highly accurate estimate based on standard input values but should be used as a guide rather than the sole determinant, especially in complex or critical applications.
Yes, it is versatile but best verified against manufacturer’s specifications or with a professional for non-standard transformers.