A wire gauge calculator simplifies the process of selecting the correct wire size for electrical circuits. By inputting the current (in amps) and the length of the wire (in feet), users can quickly determine the appropriate wire gauge, ensuring safety and minimizing energy losses in electrical systems.
Formula of Wire Gauge Calculator
To calculate wire gauge for a 12-volt system, use the following formula:
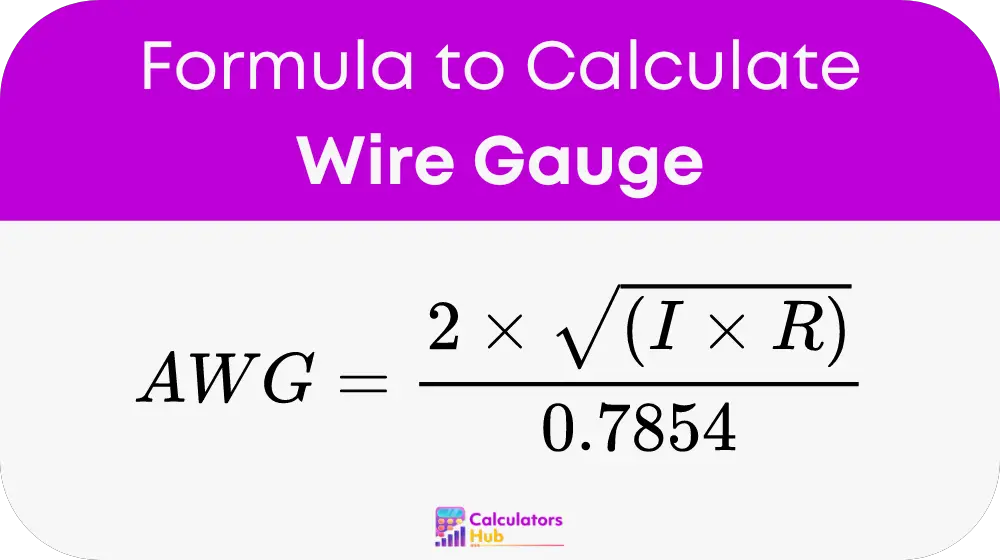
Where:
- I is the current in amps
- R is the length of the wire in feet
This formula factors in a maximum voltage drop of 3%, ensuring that the wire selection meets safety and performance standards. It's crucial to consider additional variables such as ambient temperature, insulation type, and specific application requirements.
Table of Common Wire Gauges and Their Applications
Below is a table that provides a quick reference for common wire gauges and their maximum current capacities. This table serves as a practical guide for those who wish to avoid manual calculations and ensure compliance with safety standards.
| Wire Gauge (AWG) | Max Current (Amps) |
|---|---|
| 14 | 15 |
| 12 | 20 |
| 10 | 30 |
| 8 | 40 |
| 6 | 55 |
| 4 | 70 |
| 2 | 95 |
Example of Wire Gauge Calculator
Let's calculate the appropriate wire gauge for a circuit that needs to carry 20 amps over a distance of 50 feet using a 12-volt system. Applying the formula:
Wire gauge (AWG) = (2 * √(20 * 50)) / 0.7854 = 16.01
Thus, a wire gauge of 16 AWG would be suitable for this application.
Most Common FAQs
For most home appliances, a wire gauge of 12 to 14 AWG is recommended to safely handle the typical current requirements.
Longer wire lengths require thicker gauges to minimize voltage drops and prevent overheating.
Using a higher gauge wire (thinner) than recommended can lead to increased resistance, heat buildup, and potential hazards. It is always safer to use the gauge size advised by the calculator or even one size thicker.