dBm, or decibel-milliwatts, is an absolute unit measuring power level using a logarithmic scale. The Volts to dBm calculator helps convert the voltage (measured in volts) and resistance (measured in ohms) into power readings (dBm). This tool is indispensable for professionals who require precise power measurements without delving into complex manual calculations.
Formula of Volts to dBm Calculator
To convert voltage to dBm, use the following formula:
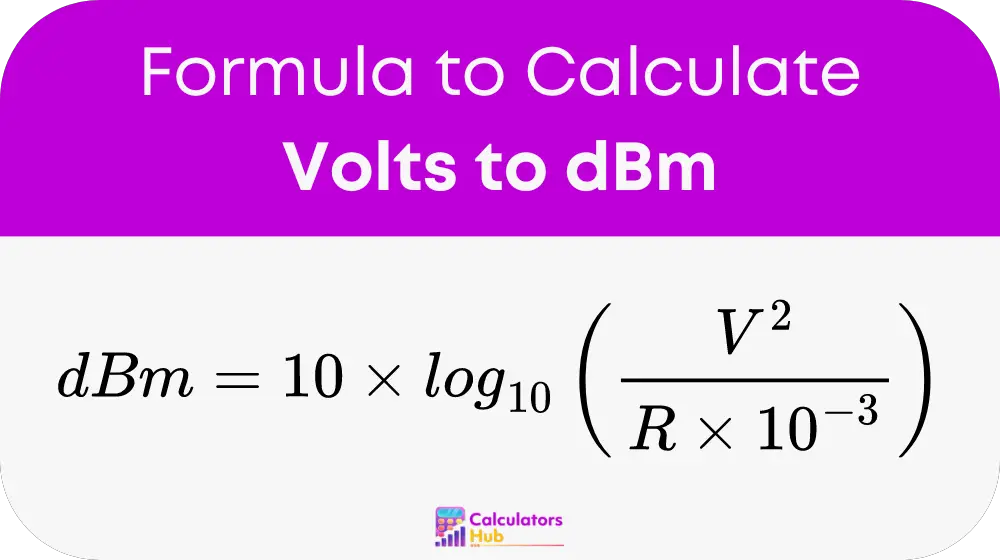
- dbm: The power in decibels relative to one milliwatt (dBm).
- v: The voltage in volts (V).
- r: The resistance in ohms (Ω).
This formula calculates the logarithm of the power ratio, providing a dBm value that indicates the power level of the signal or system in question.
Conversion Table
For convenience, here’s a table with common conversions:
| Voltage (V) | Resistance (Ω) | Power (dBm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 | -16.9897 |
| 2 | 50 | -10.9691 |
| 5 | 50 | 6.9897 |
| 1 | 75 | -13.2397 |
| 2 | 75 | -7.2191 |
| 5 | 75 | 10.7397 |
Example of Volts to dBm Calculator
Let’s calculate the dBm for 5 volts across 50 ohms:
- Calculate the power in watts (P): P = V^2 / R = 5^2 / 50 = 0.5 W
- Convert watts to milliwatts: 0.5 W = 500 mW
- Use the dBm formula: dbm = 10 * log_10(500) = 26.9897 dBm
This result shows that 5 volts across 50 ohms produces a power level of approximately 27 dBm.
Most Common FAQs
dBm measures power levels relative to one milliwatt. It’s crucial for assessing signal strength and ensuring compatible signal levels in systems.
Voltage, when combined with resistance, determines the power in a system, which can be expressed in dBm using the calculator.
Yes, but ensure the values are within practical limits for your specific application to avoid errors and ensure accuracy.