The turns ratio of a transformer is a fundamental aspect that determines its ability to convert voltage from one level to another efficiently. This ratio is defined as the number of turns of wire around the primary coil divided by the number of turns around the secondary coil. Understanding and calculating this ratio correctly ensures that transformers operate at optimal efficiency and safety standards.
Formula of Transformer Turns Ratio Calculator
To determine the turns ratio, we use the formula:
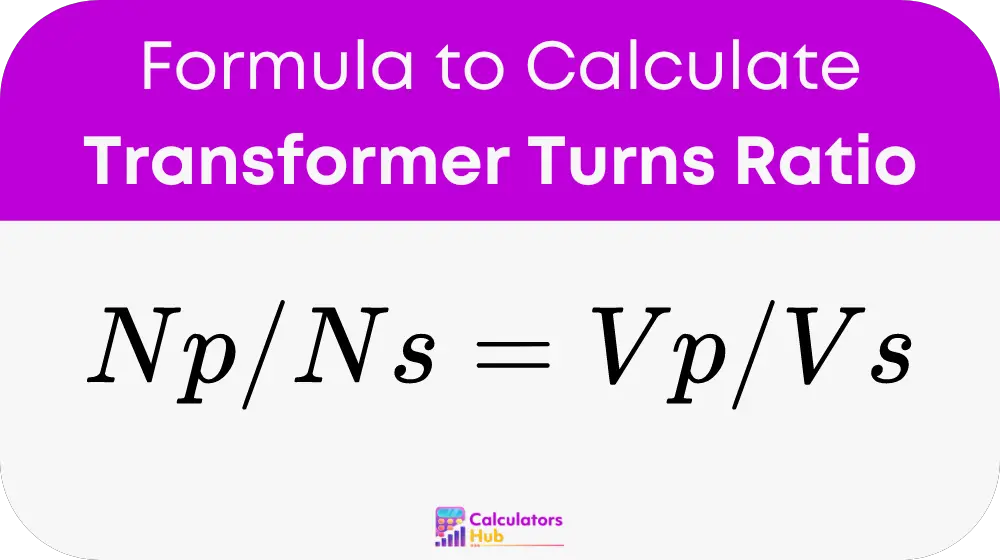
Where:
- Np is the number of turns in the primary coil (input side) of the transformer.
- Ns is the number of turns in the secondary coil (output side).
- Vp is the voltage across the primary coil.
- Vs is the voltage across the secondary coil.
This formula is crucial for anyone working with transformers as it helps predict how a transformer will alter voltage levels between its primary and secondary coils.
Helpful Tables and Conversion Tools
Table: Typical Transformer Turns Ratios
| Transformer Type | Typical Turns Ratio | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Step-up | 1:2 | Increases voltage from primary to secondary |
| Step-down | 2:1 | Decreases voltage from primary to secondary |
| Isolation | 1:1 | Maintains equal voltage across the coils |
| Auto-transformer | Variable | Uses part of the same winding as both primary and secondary |
Example of Transformer Turns Ratio Calculator
Consider a transformer designed to step down the voltage from 240 volts to 120 volts with a primary coil having 100 turns. Using our formula:
Np/Ns = Vp/Vs
100/Ns = 240/120
Calculating, we find that Ns = 50 turns. This example demonstrates how the calculator can be used in real-world applications to ensure correct transformer functionality.
Most Common FAQs
It determines how effectively a transformer can convert one voltage level to another without significant losses.
A correctly calculated turns ratio ensures maximum efficiency by minimizing energy losses during voltage conversion.
Ensure accurate measurements of voltage and precise counting of coil turns. Errors in these inputs can lead to significant performance issues.