The eV to kJ/mol Calculator is a scientific conversion tool that translates energy values from electronvolts (eV) to kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol). This conversion is particularly important in chemistry, physics, materials science, and quantum mechanics, where energy levels of atoms, bonds, and particles are often measured in eV but need to be applied in molar energy units for broader scientific or engineering use.
Researchers, educators, and students frequently use this calculator to compare molecular bond energies, reaction enthalpies, and spectroscopic data. Since energy in eV relates to single particles and kJ/mol refers to macroscopic amounts (per mole), the calculator bridges microscopic observations with practical applications.
Formula of Ev To Kj/Mol Calculator
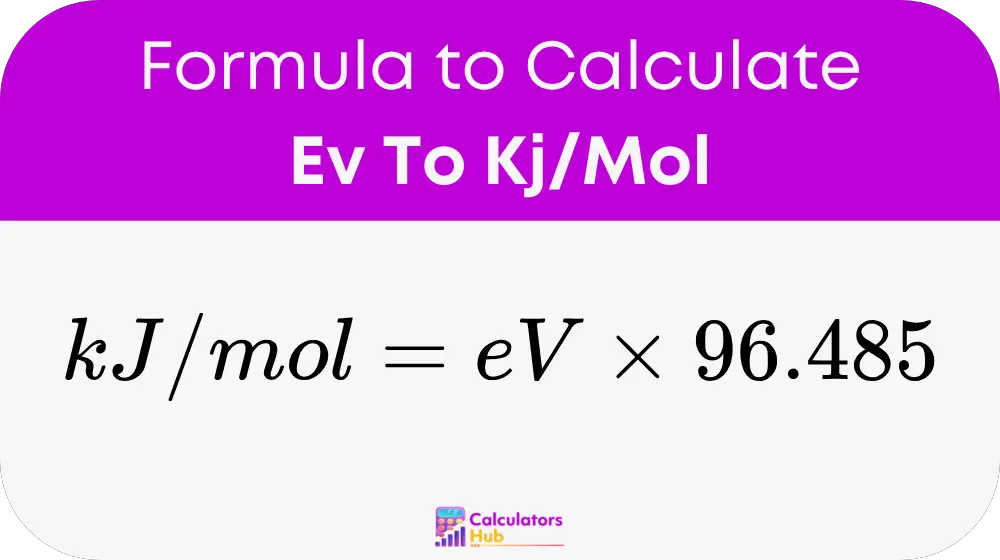
Where:
- eV is the energy value in electronvolts
- 96.485 is the conversion factor (1 eV = 96.485 kJ/mol)
Derivation of Conversion Factor:
1 eV = 1.60218 × 10⁻¹⁹ joules (energy of one electronvolt)
Multiply by Avogadro’s number (6.02214 × 10²³ mol⁻¹) to get energy per mole:
= (1.60218 × 10⁻¹⁹) × (6.02214 × 10²³) = 96,485 J/mol
Convert to kilojoules:
= 96.485 kJ/mol
This factor standardizes the conversion across scientific disciplines and ensures accurate comparison between particle-scale and bulk-scale energies.
Helpful Reference Table
Here’s a quick lookup table for converting commonly encountered eV values to kJ/mol:
| Energy (eV) | Energy (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|
| 0.1 | 9.6485 |
| 0.5 | 48.2425 |
| 1.0 | 96.485 |
| 2.5 | 241.2125 |
| 5.0 | 482.425 |
| 10.0 | 964.85 |
This table is helpful in quick estimations without needing a calculator.
Example of Ev To Kj/Mol Calculator
Let’s convert an energy value of 2.3 eV into kilojoules per mole.
Step 1: Use the conversion formula
kJ/mol = 2.3 × 96.485 = 221.9055
Result:
2.3 eV = 221.91 kJ/mol (rounded to two decimal places)
This result can now be directly compared with chemical bond energies listed in kJ/mol in standard data tables.
Most Common FAQs
eV is suitable for describing energies of individual atoms, electrons, and particles, while kJ/mol is more practical for laboratory and bulk chemistry involving macroscopic quantities of matter. The conversion connects atomic-scale measurements to real-world applications.
Yes. The conversion factor 96.485 is based on physical constants, but small variations might occur due to rounding. For high-precision calculations, use the full values of the elementary charge and Avogadro’s number.
Yes. Use the inverse of the conversion factor:
eV = kJ/mol ÷ 96.485
This lets you calculate the energy per particle from a macroscopic energy value.