The Emitter Resistance Calculator is a tool used to calculate the resistance in the emitter leg of a transistor circuit, specifically in a bipolar junction transistor (BJT). The emitter resistance plays a critical role in setting the operating point of the transistor, which affects the stability and performance of the circuit. By calculating the emitter resistance, engineers and technicians can ensure the proper functioning of transistors in various applications, such as amplification circuits, switching circuits, and signal processing systems.
The calculator uses the base-emitter voltage (Vbe) and the emitter current (Ie) to determine the emitter resistance (Re). This tool helps users quickly calculate and optimize their circuit design, improving efficiency and stability while reducing the need for manual calculations.
Formula of Emitter Resistance Calculator
The formula for calculating the emitter resistance is:
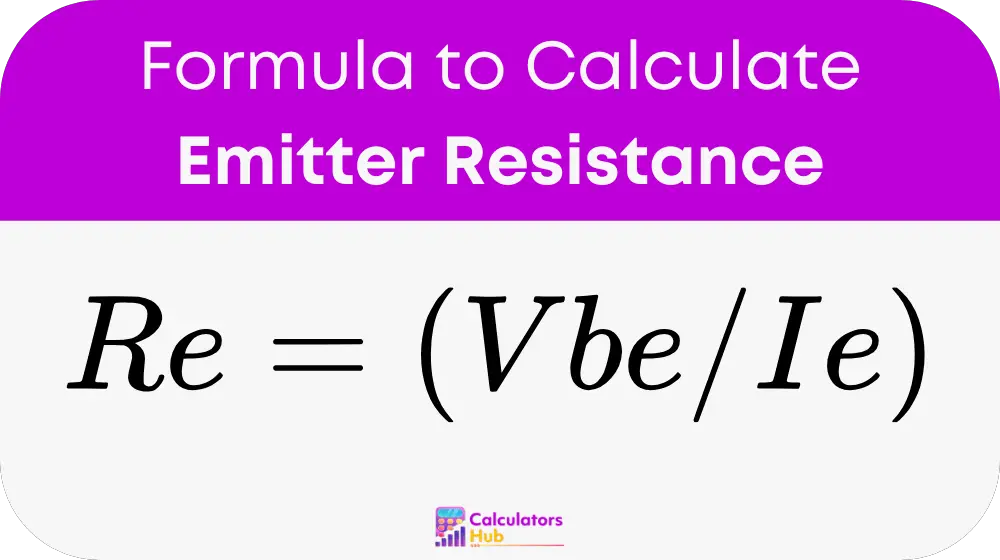
Where:
- Re is the emitter resistance, measured in ohms (Ω).
- Vbe is the base-emitter voltage of the transistor, measured in volts (V).
- Ie is the emitter current, measured in amperes (A).
This formula allows users to calculate the emitter resistance based on the voltage and current values, which is essential for understanding and controlling the performance of BJT circuits.
Common Search Terms and Helpful Conversion Table
Here’s a table with general terms and units related to emitter resistance and transistor circuits. This table can help users understand the variables involved and ensure accurate calculations:
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Emitter Resistance (Re) | The resistance between the emitter and ground in a transistor circuit. It is essential for setting the operating point of the transistor. |
| Base-Emitter Voltage (Vbe) | The voltage between the base and emitter terminals of a transistor. It typically ranges from 0.6V to 0.7V for silicon BJTs. |
| Emitter Current (Ie) | The current flowing through the emitter of a transistor. This current controls the transistor's operation and amplification. |
| Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) | A type of transistor commonly used for amplification and switching. It has three terminals: base, emitter, and collector. |
| Operating Point | The point in a transistor's characteristic curve where it operates under a given set of voltage and current conditions. |
| Amplification Circuit | A circuit that uses a transistor to amplify weak electrical signals to higher levels. |
This table helps users better understand the terms and concepts related to the emitter resistance calculation and the functioning of transistor circuits.
Example of Emitter Resistance Calculator
Let’s walk through an example to demonstrate how the Emitter Resistance Calculator works.
Scenario:
- Vbe (Base-Emitter Voltage) = 0.7 V (a typical value for silicon BJTs)
- Ie (Emitter Current) = 10 mA (0.01 A)
Using the formula:
Re = Vbe / Ie
Re = 0.7 V / 0.01 A = 70 Ω
In this example, the emitter resistance is 70 ohms, which means that the resistance in the emitter leg of the transistor is 70 Ω when the base-emitter voltage is 0.7 V and the emitter current is 10 mA. This value is crucial for setting the correct operating point of the transistor and ensuring optimal circuit performance.
Most Common FAQs
Emitter resistance (Re) is the resistance in the emitter leg of a transistor circuit. It is essential for controlling the current flowing through the transistor and ensuring that the transistor operates within its intended parameters. Proper emitter resistance helps stabilize the operating point of the transistor, improving the performance and efficiency of the circuit.
To calculate the emitter resistance, use the formula Re = Vbe / Ie, where Vbe is the base-emitter voltage, and Ie is the emitter current. These values can be obtained from the transistor's operating conditions and are essential for ensuring the correct operation of the transistor.
Emitter resistance affects the current flowing through the transistor, which in turn influences the transistor’s amplification and switching capabilities. Proper emitter resistance helps maintain the stability of the transistor’s operating point, ensuring that the transistor functions efficiently in amplification circuits and other applications.