The Dual Voltage Transformer Calculator finds the secondary voltage—the output you get from a transformer—based on the input voltage and the number of turns in its coils. You enter the primary voltage and the turns for both the primary and secondary windings, and it gives you the result. This is super helpful for real-life tasks, like designing circuits, fixing equipment, or ensuring safe power use.
This calculator saves time and prevents mistakes, especially when you need the right voltage for a job. It’s reliable for important decisions, like picking the correct transformer for your project. Want to know how it’s done? Let’s check out the formula next.
Formula for Dual Voltage Transformer
Calculating the secondary voltage is simple with this formula:
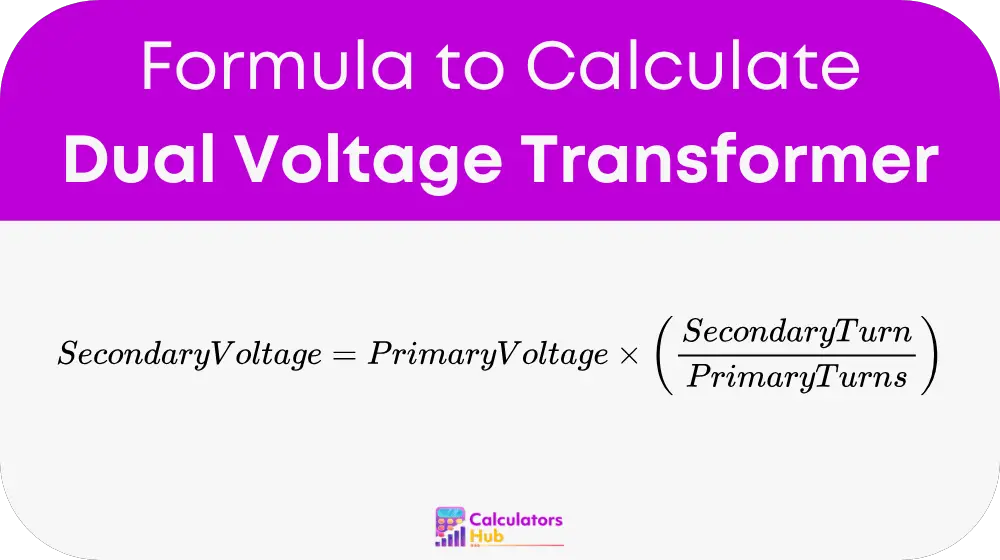
Where:
- Secondary Voltage is the output voltage (in volts)
- Primary Voltage is the input voltage (in volts)
- Secondary Turns is the number of turns in the secondary winding
- Primary Turns is the number of turns in the primary winding
This formula comes from basic transformer principles: the voltage changes based on the ratio of turns. More turns on the secondary side increase the voltage, while fewer turns decrease it. Now, let’s make it easier with a table.
Quick Reference Table for Dual Voltage Transformers
Why calculate every time? This table shows common transformer setups and their output voltages. It’s a quick way to plan without doing math each time.
| Primary Voltage (V) | Primary Turns | Secondary Turns | Secondary Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 120 | 100 | 200 | 240 |
| 240 | 200 | 100 | 120 |
| 110 | 50 | 150 | 330 |
| 220 | 100 | 50 | 110 |
How to Use the Table
- Find your primary voltage and turns.
- Check the secondary turns.
- Use the secondary voltage for your setup.
This table helps with searches like “transformer 120V to 240V.” For other values, use the formula. Next, let’s try an example.
Example of Dual Voltage Transformer Calculator
Suppose you have a transformer with a primary voltage of 120 volts. The primary winding has 80 turns, and the secondary winding has 160 turns. You want to know the output voltage. Here’s how to do it:
- Plug into the formula:
Secondary Voltage = Primary Voltage × (Secondary Turns ÷ Primary Turns) - Divide the turns:
160 ÷ 80 = 2 - Multiply by primary voltage:
Secondary Voltage = 120 × 2 = 240 volts
So, the secondary voltage is 240 volts. This matches transformer rules and shows how the turns ratio doubles the voltage.
Most Common FAQs
This calculator is for dual voltage setups. For more voltages, calculate each pair separately.
Yes, as long as you know the primary and secondary turns and voltage, it works for any basic transformer.
The turns control how much the voltage changes—more secondary turns mean higher voltage, fewer mean lower.