The Dielectric Strength Calculator helps determine the maximum electric field an insulating material can withstand before it fails and starts conducting electricity. This calculation is crucial for designing electrical insulation systems, ensuring materials can safely handle applied voltages without breakdown. Engineers, physicists, and material scientists use dielectric strength calculations to select the right insulating materials for applications like transformers, capacitors, high-voltage power lines, and electronic circuits.
By inputting breakdown voltage and material thickness, this calculator provides a dielectric strength value that helps evaluate the performance and reliability of insulating materials.
Formula of Dielectric Strength Calculator
The dielectric strength of a material is calculated using the formula:
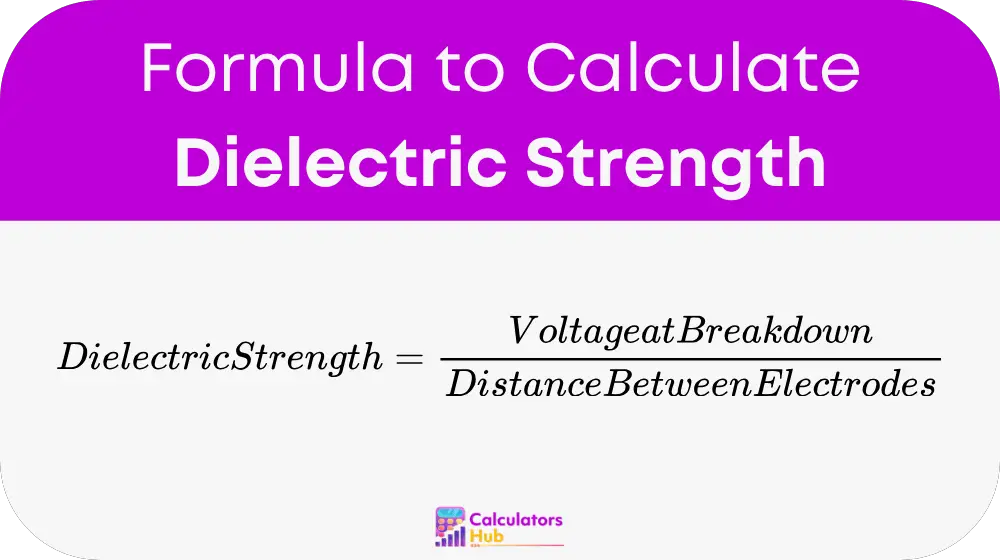
where:
Breakdown Voltage is the voltage at which an insulating material fails and starts conducting electricity. It is usually measured in volts V or kilovolts kV
Material Thickness mm or cm is the thickness of the insulating material separating two conductive electrodes
Distance Between Electrodes mm or cm is the separation distance between two electrodes applying the voltage
The dielectric strength is typically expressed in volts per unit thickness V/mm or kV/cm Higher values indicate better insulating properties
Dielectric Strength Reference Table
This table provides estimated dielectric strength values for common insulating materials The values can help users compare different materials when selecting electrical insulation
Material Dielectric Strength kV/mm Application Air 3.0 High-voltage circuits Glass 9.0 - 40.0 Electrical insulators, displays PVC 19.0 - 40.0 Wire insulation Rubber 10.0 - 20.0 Cable insulation, gloves Teflon PTFE 60.0 High-frequency applications Transformer Oil 12.0 - 50.0 Electrical transformers Mica 100.0 - 200.0 Capacitors, electrical insulation Silicon 20.0 - 30.0 Semiconductor applications
These values vary based on environmental factors, material purity, and measurement conditions
Example of Dielectric Strength Calculator
Scenario An electrical engineer is designing an insulating layer for a high-voltage application The breakdown voltage of the material is 50 kV and the material thickness is 5 mm
Solution Using the formula:
Dielectric Strength = Voltage at Breakdown / Distance Between Electrodes
Dielectric Strength = 50 kV / 5 mm = 10 kV/mm
Result The material has a dielectric strength of 10 kV/mm meaning it can withstand 10000 volts per millimeter before breaking down
Most Common FAQs
Dielectric strength determines how well an insulating material can prevent electrical breakdown. It ensures that materials use in electrical systems do not fail under high voltage preventing short circuits fires and equipment damage
Higher temperatures can reduce dielectric strength by increasing material conductivity. In contrast some materials improve their insulating properties at lower temperatures Engineers must consider temperature variations when selecting insulation materials
Yes aging moisture absorption contamination and repeated exposure to high voltage can degrade a material’s dielectric strength Regular maintenance and testing help ensure reliability in electrical insulation systems